Efficient translation of Eggplant mottled dwarf nucleorhabdovirus N and X genes requires both 5' and 3' UTRs
- PMID: 34174907
- PMCID: PMC8236180
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-021-01601-4
Efficient translation of Eggplant mottled dwarf nucleorhabdovirus N and X genes requires both 5' and 3' UTRs
Abstract
Background: Circularization of RNA mediated by association of translation factors and RNA elements in 5' and 3' UTRs is a common feature for translation control in eukaryotes. There is no information about translation in plant rhabdoviruses and little information is known in animal rhabdoviruses.
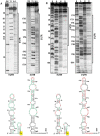
Methods: The role of 5' and 3' UTRs in two genes of EMDV in translation were studied using luciferase constructs and RNA structures of these sequences were analyzed by SHAPE and Inline probing.
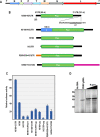
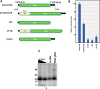
Results: We have found that efficient translation of N and X mRNAs of nucleorhabdovirus Eggplant mottled dwarf virus (EMDV) requires elements present in both 5' and 3' UTRs. Luciferase reporter constructs containing precise 5' and 3' UTRs of the N and X genes had substantially higher translational activity compared with constructs containing only the 5' or 3' UTR. The 3'UTR of carmovirus Turnip crinkle virus, which contains a well-characterized cap-independent translation enhancer, was unable to complement the lack of EMDV 3' UTR. Addition of cap analog to luciferase constructs containing the UTRs of the N gene did not restore translation, and translation of the reporter construct in the absence of the 5' cap was higher than the capped construct. No RNA-RNA interactions between 5' and 3' UTRs were detected by EMSA or in-line cleavage structural assays. Deletion of 11 nucleotides from the 3' terminus negated the synergistic activity of the 3'UTR.
Conclusions: The results with RNA-RNA interaction suggesting that translational synergy between the UTRs may utilize alternative means. Mutation analysis in 3'UTR suggesting that the polyadenylation signal sequence contained in this location may play a critical role in translation.
Keywords: Eggplant mottled dwarf virus; Rhabdovirus; Translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Babaie Gh, Izadpanah K. Host range, distribution, isolates and transmission trials of Eggplant mottled dwarf virus. Iran J Plant Pathol. 2002;38:235–250.
-
- Babaie GH, Izadpanah K. Vector transmission of Eggplant mottled dwarf virus in Iran. J Phytopathol. 2003;151:679–682. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0434.2003.00788.x. - DOI
-
- Babaie Gh, Kouhi Habibi M, Massah A, Dizadji A, et al. Complete genome sequence and genome analysis of Eggplant mottled dwarf virus-Iranian Isolate. J Phytopathol. 2015;163:331–341. doi: 10.1111/jph.12256. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

