Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels and responses of pancreatic islet β-cells and α-cells in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 34174950
- PMCID: PMC8234651
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-021-00690-z
Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels and responses of pancreatic islet β-cells and α-cells in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4), as an intracellular lipid chaperone and adipokine, was reported to be related to the incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and diabetic complications, but its association with pancreatic islet β-cell and α-cell functions has not been fully elucidated. So the present study was to investigate the serum FABP4 levels and responses of islet β-cells and α-cells in patients with T2D.
Methods: 115 patients with T2D and 89 healthy controls (HC), who received serum FABP4 levels test, were recruited to participate in this study. Moreover, 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed in T2D patients to evaluate islet β-cell and α-cell functions. Systemic insulin sensitivity and overall insulin secretion of islet β-cell function were assessed by Matsuda index using C peptide (ISIM-cp) and ratio of the area under the C peptide curve to the glucose curve (AUCcp/glu) during OGTT, respectively. Fasting glucagon (Gluca0min) and postchallenge glucagon assessed by the area under the glucagon curve (AUCgluca) were determined during OGTT to evaluate islet α-cell function. And other various clinical variables were also measured in all participants. Skewed variables were natural log-transformed (ln), such as lnFABP4.
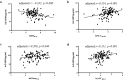
Results: The serum FABP4 levels in T2D patients were significantly higher than those in HC (p < 0.05). And after partially adjusting for fasting plasma glucose, serum lnFABP4 levels were negatively correlated with lnISIM-cp (r = - 0.332, p < 0.001) and positively correlated with lnAUCcp/glu (r = 0.324, p < 0.001), lnGluca0min (r = 0.200, p = 0.040) and lnAUCgluca (r = 0.311, p < 0.001), respectively, in patients with T2D. Furthermore, when multiple linear regression analyses were applied to adjust for other various clinical variables, serum lnFABP4 levels were found to remain associated with lnISIM-cp (β = - 0.296, t = - 2.900, p = 0.005), lnAUCcp/glu (β = 0.223, t = 2.038, p = 0.046), lnGluca0min (β = 0.272, t = 2.330, p = 0.024) and lnAUCgluca (β = 0.341, t = 3.065, p = 0.004), respectively.
Conclusion: Increased serum FABP4 levels were closely associated with blunted insulin sensitivity, increased insulin secretion, and elevated fasting and postchallenge glucagon levels in patients with T2D.
Keywords: FABP4; Type 2 diabetes; α-cell function; β-cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fasting serum total bile acid levels are associated with insulin sensitivity, islet β-cell function and glucagon levels in response to glucose challenge in patients with type 2 diabetes.Endocr J. 2020 Nov 28;67(11):1107-1117. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0201. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 32684527
-
Increased serum cystatin C levels and responses of pancreatic α- and β-cells in type 2 diabetes.Endocr Connect. 2022 Mar 21;11(3):e210597. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0597. Endocr Connect. 2022. PMID: 35179515 Free PMC article.
-
Inverse relationship between serum adenosine deaminase levels and islet beta cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021 May 17;13(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13098-021-00671-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021. PMID: 34001220 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of the gut in diabetic hyperglucagonaemia.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5340. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385175 Review.
-
Animal Models for Understanding the Mechanisms of Beta Cell Death during Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 20;12(3):473. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030473. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Nrf2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism rs35652124 and FABP4 Levels with Peripheral Artery Disease Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Pakistani Population.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 9;47(7):530. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070530. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728998 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Roles of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 (FABP4) in Fetal and Maternal Health and Maintenance of Pregnancy in Women with Obesity: A Review.Med Sci Monit. 2025 Jun 30;31:e947679. doi: 10.12659/MSM.947679. Med Sci Monit. 2025. PMID: 40583243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FABP4 and I-FABP Levels in Pregnant Women Are Associated with Body Mass Index but Not Gestational Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2022 May 20;2022:1089434. doi: 10.1155/2022/1089434. eCollection 2022. J Diabetes Res. 2022. PMID: 35647197 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-Organ Crosstalk in the Development of Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;274:205-226. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_564. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34853949
-
The role of the beta cell in type 2 diabetes: new findings from the last 5 years.Diabetologia. 2025 Aug 6. doi: 10.1007/s00125-025-06499-z. Online ahead of print. Diabetologia. 2025. PMID: 40768044 Review.
References
-
- Knop FK, Vilsboll T, Madsbad S, Holst JJ, Krarup T. Inappropriate suppression of glucagon during OGTT but not during isoglycaemic i.v. glucose infusion contributes to the reduced incretin effect in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2007;50:797–805. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0566-z. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

