Porcine small intestinal organoids as a model to explore ETEC-host interactions in the gut
- PMID: 34174960
- PMCID: PMC8235647
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-021-00961-7
Porcine small intestinal organoids as a model to explore ETEC-host interactions in the gut
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Porcine small intestinal organoids as a model to explore ETEC-host interactions in the gut.Vet Res. 2021 Aug 3;52(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00977-z. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34344443 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
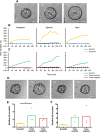
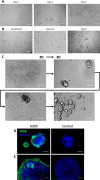
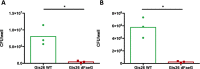
Small intestinal organoids, or enteroids, represent a valuable model to study host-pathogen interactions at the intestinal epithelial surface. Much research has been done on murine and human enteroids, however only a handful studies evaluated the development of enteroids in other species. Porcine enteroid cultures have been described, but little is known about their functional responses to specific pathogens or their associated virulence factors. Here, we report that porcine enteroids respond in a similar manner as in vivo gut tissues to enterotoxins derived from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, an enteric pathogen causing postweaning diarrhoea in piglets. Upon enterotoxin stimulation, these enteroids not only display a dysregulated electrolyte and water balance as shown by their swelling, but also secrete inflammation markers. Porcine enteroids grown as a 2D-monolayer supported the adhesion of an F4+ ETEC strain. Hence, these enteroids closely mimic in vivo intestinal epithelial responses to gut pathogens and are a promising model to study host-pathogen interactions in the pig gut. Insights obtained with this model might accelerate the design of veterinary therapeutics aimed at improving gut health.
Keywords: ETEC; Enteroids; Intestinal stem cells; Pig; Swelling assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
I-FABP, Pig-MAP and TNF-α as biomarkers for monitoring gut-wall integrity in front of Salmonella Typhimurium and ETEC K88 infection in a weaned piglet model.Res Vet Sci. 2019 Jun;124:426-432. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 7. Res Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31082572
-
Regional differences in the effect of cholera toxin and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection on electrolyte and fluid transport in the porcine small intestine.Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1998 Sep;45(6-7):369-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0442.1998.tb00840.x. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1998. PMID: 9793468
-
Mechanical Stimuli Affect Escherichia coli Heat-Stable Enterotoxin-Cyclic GMP Signaling in a Human Enteroid Intestine-Chip Model.Infect Immun. 2020 Feb 20;88(3):e00866-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00866-19. Print 2020 Feb 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 31818966 Free PMC article.
-
Small intestinal segment perfusion test in piglets: future applications in studying probiotics-gut crosstalk in infectious diarrhoea?Benef Microbes. 2010 Nov;1(4):439-45. doi: 10.3920/BM2010.0025. Benef Microbes. 2010. PMID: 21831782 Review.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in farm animals.Vet Res. 1999 Mar-Jun;30(2-3):259-84. Vet Res. 1999. PMID: 10367358 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal organoids as advanced modeling platforms to study the role of host-microbiome interaction in homeostasis and disease.BMB Rep. 2023 Jan;56(1):15-23. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022-0182. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 36379514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualizing the internalization and biological impact of nanoplastics in live intestinal organoids by Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM).Light Sci Appl. 2025 Aug 12;14(1):272. doi: 10.1038/s41377-025-01949-0. Light Sci Appl. 2025. PMID: 40796554 Free PMC article.
-
Farm and Companion Animal Organoid Models in Translational Research: A Powerful Tool to Bridge the Gap Between Mice and Humans.Front Med Technol. 2022 May 12;4:895379. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2022.895379. eCollection 2022. Front Med Technol. 2022. PMID: 35647577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing and CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli BE311 for Fluorescence Labeling and Enterotoxin Analyses.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 6;23(14):7502. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147502. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886856 Free PMC article.
-
Culture media and format alter cellular composition and barrier integrity of porcine colonoid-derived monolayers.Tissue Barriers. 2024 Apr 2;12(2):2222632. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2023.2222632. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Tissue Barriers. 2024. PMID: 37340938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melkebeek V, Goddeeris BM, Cox E. ETEC vaccination in pigs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2013;152:37–42. - PubMed
-
- Sjölund M, Zoric M, Wallgren P (2014) Financial impact on pig production: III. Gastrointestinal disorders. In: University of Parma (Italy) (ed) 6th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management. Sorrento, Italy, pp. 189
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

