Structural basis of NF-κB signaling by the p75 neurotrophin receptor interaction with adaptor protein TRADD through their respective death domains
- PMID: 34175311
- PMCID: PMC8318917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100916
Structural basis of NF-κB signaling by the p75 neurotrophin receptor interaction with adaptor protein TRADD through their respective death domains
Erratum in
-
Correction: Structural basis of NF-κB signaling by the p75 neurotrophin receptor interaction with adaptor protein TRADD through their respective death domains.J Biol Chem. 2022 Nov;298(11):102583. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102583. Epub 2022 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36257251 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
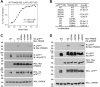
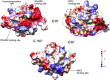
The p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) is a critical mediator of neuronal death and tissue remodeling and has been implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases and cancers. The death domain (DD) of p75NTR is an intracellular signaling hub and has been shown to interact with diverse adaptor proteins. In breast cancer cells, binding of the adaptor protein TRADD to p75NTR depends on nerve growth factor and promotes cell survival. However, the structural mechanism and functional significance of TRADD recruitment in neuronal p75NTR signaling remain poorly understood. Here we report an NMR structure of the p75NTR-DD and TRADD-DD complex and reveal the mechanism of specific recognition of the TRADD-DD by the p75NTR-DD mainly through electrostatic interactions. Furthermore, we identified spatiotemporal overlap of p75NTR and TRADD expression in developing cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) at early postnatal stages and discover the physiological relevance of the interaction between TRADD and p75NTR in the regulation of canonical NF-κB signaling and cell survival in CGNs. Our results provide a new structural framework for understanding how the recruitment of TRADD to p75NTR through DD interactions creates a membrane-proximal platform, which can be efficiently regulated by various neurotrophic factors through extracellular domains of p75NTR, to propagate downstream signaling in developing neurons.
Keywords: NMR; TRADD; cell signaling; death domain; p75 neurotrophin receptor; protein structure.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this manuscript.
Figures
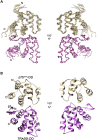
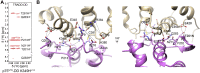



Similar articles
-
Structure of the C-terminal domain of TRADD reveals a novel fold in the death domain superfamily.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 1;7(1):7073. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07348-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28765645 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotypic interactions among members of the death domain superfamily with implications for p75NTR-mediated co-signaling.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;304(Pt 1):140791. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140791. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39924025
-
Structural Characterization of the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor: A Stranger in the TNFR Superfamily.Vitam Horm. 2017;104:57-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Vitam Horm. 2017. PMID: 28215307 Review.
-
Death Domain Signaling by Disulfide-Linked Dimers of the p75 Neurotrophin Receptor Mediates Neuronal Death in the CNS.J Neurosci. 2016 May 18;36(20):5587-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4536-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27194337 Free PMC article.
-
Death domain of p75 neurotrophin receptor: a structural perspective on an intracellular signalling hub.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019 Aug;94(4):1282-1293. doi: 10.1111/brv.12502. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2019. PMID: 30762293 Review.
Cited by
-
The functional and molecular roles of p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) in epilepsy.J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2024 Apr 22;16:11795735241247810. doi: 10.1177/11795735241247810. eCollection 2024. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2024. PMID: 38655152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Pathway of p75 Neurotrophin Receptor (p75NTR) in Parkinson's Disease: The Way of New Inroads.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May;61(5):2469-2480. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03727-8. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37897634 Review.
-
A structural atlas of death domain fold proteins reveals their versatile roles in biology and function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 25;122(8):e2426986122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2426986122. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39977327 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve Growth Factor and Autoimmune Diseases.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 10;45(11):8950-8973. doi: 10.3390/cimb45110562. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37998739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Neurotrophic Factors as a Promising Strategy for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases (Review).Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024 Aug;177(4):517-527. doi: 10.1007/s10517-024-06218-5. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39266924 Review.
References
-
- Chao M.V., Bothwell M.A., Ross A.H., Koprowski H., Lanahan A.A., Buck C.R., Sehgal A. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the human NGF receptor. Science. 1986;232:518–521. - PubMed
-
- Johnson D., Lanahan A., Buck C.R., Sehgal A., Morgan C., Mercer E., Bothwell M., Chao M. Expression and structure of the human NGF receptor. Cell. 1986;47:545–554. - PubMed
-
- Radeke M.J., Misko T.P., Hsu C., Herzenberg L.A., Shooter E.M. Gene transfer and molecular cloning of the rat nerve growth factor receptor. Nature. 1987;325:593–597. - PubMed
-
- Ibanez C.F., Simi A. p75 neurotrophin receptor signaling in nervous system injury and degeneration: paradox and opportunity. Trends Neurosci. 2012;35:431–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

