Sex Differences in Pulmonary Eicosanoids and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Response to Ozone Exposure
- PMID: 34175951
- PMCID: PMC8404991
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfab081
Sex Differences in Pulmonary Eicosanoids and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Response to Ozone Exposure
Abstract
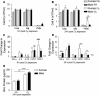
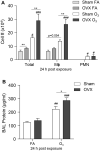
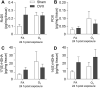
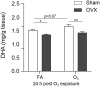
Ozone (O3) is a criteria air pollutant known to increase the morbidity and mortality of cardiopulmonary diseases. This occurs through a pulmonary inflammatory response characterized by increased recruitment of immune cells into the airspace, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and pro-inflammatory lipid mediators. Recent evidence has demonstrated sex-dependent differences in the O3-induced pulmonary inflammatory response. However, it is unknown if this dimorphic response is evident in pulmonary lipid mediator metabolism. We hypothesized that there are sex-dependent differences in lipid mediator production following acute O3 exposure. Male and female C57BL/6J mice were exposed to 1 part per million O3 for 3 h and were necropsied at 6 or 24 h following exposure. Lung lavage was collected for cell differential and total protein analysis, and lung tissue was collected for mRNA analysis, metabololipidomics, and immunohistochemistry. Compared with males, O3-exposed female mice had increases in airspace neutrophilia, neutrophil chemokine mRNA, pro-inflammatory eicosanoids such as prostaglandin E2, and specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), such as resolvin D5 in lung tissue. Likewise, precursor fatty acids (arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid; DHA) were increased in female lung tissue following O3 exposure compared with males. Experiments with ovariectomized females revealed that loss of ovarian hormones exacerbates pulmonary inflammation and injury. However, eicosanoid and SPM production were not altered by ovariectomy despite depleted pulmonary DHA concentrations. Taken together, these data indicate that O3 drives an increased pulmonary inflammatory and bioactive lipid mediator response in females. Furthermore, ovariectomy increases susceptibility to O3-induced pulmonary inflammation and injury, as well as decreases pulmonary DHA concentrations.
Keywords: air pollution; inflammation; lipids; lung; sex differences.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology.All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators Regulate Ozone-Induced Pulmonary and Systemic Inflammation.Toxicol Sci. 2018 Jun 1;163(2):466-477. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy040. Toxicol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29471542 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Mechanisms of Ozone-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Resolution, and the Potential Protective Role of Scavenger Receptor BI.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2021 Mar;2021(204):1-49. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2021. PMID: 33998222 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic Acid and Its Metabolites Protects Against Ozone-induced Pulmonary Inflammation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 10. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0586OC. Online ahead of print. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40208640
-
Ozone-induced lung inflammation and mucosal barrier disruption: toxicology, mechanisms, and implications.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 1999 Jan-Mar;2(1):31-86. doi: 10.1080/109374099281232. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 1999. PMID: 10081525 Review.
-
Potential Clinical Applications of Pro-Resolving Lipids Mediators from Docosahexaenoic Acid.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 26;15(15):3317. doi: 10.3390/nu15153317. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-resident alveolar macrophages reduce O3-induced inflammation via MerTK mediated efferocytosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 6:2023.11.06.565865. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.06.565865. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024 Jun;70(6):493-506. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0390OC. PMID: 37986982 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Neuroendocrine contribution to sex-related variations in adverse air pollution health effects.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2024 Nov 16;27(8):287-314. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2024.2383637. Epub 2024 Jul 29. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2024. PMID: 39075643 Review.
-
The Biological and Molecular Action of Ozone and Its Derivatives: State-of-the-Art, Enhanced Scenarios, and Quality Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 9;24(10):8465. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108465. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALX/FPR2 Contributes to Serum Amyloid A-Induced Lung Neutrophil Recruitment Following Acute Ozone Exposure.FASEB J. 2025 Jun 15;39(11):e70555. doi: 10.1096/fj.202402865R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40420730 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Resident Alveolar Macrophages Reduce Ozone-induced Inflammation via MerTK-mediated Efferocytosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024 Jun;70(6):493-506. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0390OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38386777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfaro M. F., Walby W. F., Adams W. C., Schelegle E. S. (2007). Breath condensate levels of 8-isoprostane and leukotriene B4 after ozone inhalation are greater in sensitive versus nonsensitive subjects. Exp. Lung Res. 33, 115–133. - PubMed
-
- Aoki T., Narumiya S. (2012). Prostaglandins and chronic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 33, 304–311. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong M., Manke J., Nkrumah-Elie Y., Shaikh S. R., Reisdorph N. (2020). Improved quantification of lipid mediators in plasma and tissues by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry demonstrates mouse strain specific differences. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 151, 106483. - PubMed
-
- Bakewell L., Burdge G. C., Calder P. C. (2006). Polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrations in young men and women consuming their habitual diets. Br. J. Nutr. 96, 93–99. - PubMed
-
- Barden A. E., Moghaddami M., Mas E., Phillips M., Cleland L. G., Mori T. A. (2016). Specialised pro-resolving mediators of inflammation in inflammatory arthritis. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent. Fatty Acids 107, 24–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

