Protective effects of baicalin on caerulein-induced AR42J pancreatic acinar cells by attenuating oxidative stress through miR-136-5p downregulation
- PMID: 34176350
- PMCID: PMC10305831
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504211026118
Protective effects of baicalin on caerulein-induced AR42J pancreatic acinar cells by attenuating oxidative stress through miR-136-5p downregulation
Abstract
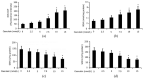
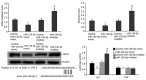
Baicalin, the main active component of Scutellaria baicalensis, has antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects and is used to treat acute pancreatitis; however, its specific mechanism is unclear. This study aims to determine the protective effect and underlying mechanism of baicalin on AR42J pancreatic acinar cell injury. AR42J acinar cells (caerulein, 10 nmol/L) were induced in vitro to establish a cell model for acute pancreatitis. Cell relative survival was measured by thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide, and cell apoptosis and death were examined by flow cytometry. The expression levels of superoxide dismutase1 (SOD1), Bax, survivin, Bcl-2, caspase-3, and caspase-7 proteins were analyzed by Western blot, and those of SOD1 mRNA and miR-136-5p were determined by RT-PCR. The activities of GSH, SOD1, ROS, and MDA were also investigated. Compared with those of the caerulein group, the relative survival rate and activity of AR42J pancreatic acinar cells with different baicalin concentrations were significantly increased (p < 0.05), and the supernatant amylase level was markedly decreased (p < 0.05). In addition, the ROS and MDA activities and mir-136-5p expression were significantly decreased, and the GSH activities and SOD1 gene and protein expression levels were markedly increased (p < 0.05). These results suggest that baicalin reduced the caerulein-induced death of AR42J acinar cells and alleviated the caerulein-induced injury in pancreatic acinar cells by inhibiting oxidative stress. The mechanism may be related to the decreased expression of Mir-136-5p and the increased expression of SOD1 gene and protein.
Keywords: AR42J acinar cells; Baicalin; acute pancreatitis; miR-136-5p; oxidative stress; superoxide dismutase 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures











References
-
- Amas Gómez L, Zubia Olaskoaga F. Results of the modification of an acute pancreatitis management protocol in Intensive Care medicine. Med Intensiva 2019; 43(9): 546–555. - PubMed
-
- Hines OJ, Pandol SJ. Management of severe acute pancreatitis. BMJ 2019; 367: l6227. - PubMed
-
- Ma Z, Song G, Zhao D, et al.. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate severe acute pancreatitis in rats via hemeoxygenase-1-mediated anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Cytotherapy 2019; 21(2): 162–174. - PubMed
-
- Máté G, Gazdag Z, Mike N, et al.. Regulation of oxidative stress-induced cytotoxic processes of citrinin in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Toxicon 2014; 90: 155–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

