Clinical and demographic features among patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Henan, China
- PMID: 34176476
- PMCID: PMC8237411
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-021-00799-2
Clinical and demographic features among patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Henan, China
Abstract
Background: The hallmark of type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an absolute lack of insulin. However, many studies showed a tendency to heterogeneity in TID. We aimed to investigate the demographic and clinical characteristics in T1D and the differences in young-onset and adult-onset patients.
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted among 1943 patients with clinically diagnosed T1D. Medical records on patients' demographics, anthropometric measurements, and clinical manifestation were collected. According to the age at onset, the newly diagnosed patients were divided into the young-onset group (< 18 years, 234 patients, mean age 11 years) and adult-onset group (≥ 18 years, 219 patients, mean age 27 years). Pancreatic β-cell function was assessed by fasting C-peptide (FCP) and 2-h C-peptide (2-h CP).
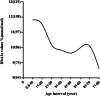
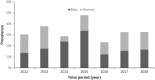
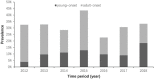
Results: The median age of patients at disease onset was 22 years. The median duration of patients was 3 years. The overall median glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) value was 10.3 % [89(mmol/mol)]. The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy was 25.1 %. The overall rate of DKA at onset in the new-onset patients was 59.6 %. The frequency of overall dyslipidemia was 37.8 %. The most frequent dyslipidemia was low high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL) (29 %). The proportion of patients with anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (GADA), insulin antibody (IAA) and islet cell antibody (ICA) were 28.1 %, 6.4 % and 21.6 %, respectively. The mean HbA1c showed a downward trend with age. Increasing or decreasing trends of overweight and obesity in this population during the period 2012 to 2018 was not found. Compared with young-onset T1D, adult-onset patients comprised better islet function (FCP: 0.4 vs. 0.3 ng/ml, P < 0.001; 2-h CP: 0.9 vs. 0.7 ng/ml P < 0.001, respectively) and glycemic control [12.9 % (117mmol/mol) vs. 11.7 % (104mmol/mol), P < 0.001], higher prevalence of diabetes condition in the male gender (64.4 % vs. 51.3 %, P = 0.006), higher proportion of obesity or overweight (24.6 % vs. 9.5 %, P = 0.002), higher frequency of GADA (33.7 % vs. 23.3 %, P = 0.025), and lower frequency of diabetic ketoacidosis at disease onset (64.5 % vs. 43.5 %, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: This population was characterized by poor overall blood glucose control, high prevalence of DKA, dyslipidemia and diabetic retinopathy, and low prevalence of islet-related antibodies, and overweight or obesity. Adult-onset patients with T1D were not uncommon and had better clinical manifestations than young-onset patients. Any findings related to body mass index (BMI) and autoantibodies should be considered strictly exploratory due to excessive missing data.
Keywords: Chinese; Epidemiology; Type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetic ketoacidosis at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and glycemic control over time: The SEARCH for diabetes in youth study.Pediatr Diabetes. 2019 Mar;20(2):172-179. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12809. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Pediatr Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 30556249 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features, biomarkers and diabetic ketoacidosis at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes among children and adolescents in Sana'a, Yemen.BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024 Aug 3;8(1):e002680. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2024-002680. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2024. PMID: 39097331 Free PMC article.
-
Multinational study in children and adolescents with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes: association of age, ketoacidosis, HLA status, and autoantibodies on residual beta-cell function and glycemic control 12 months after diagnosis.Pediatr Diabetes. 2010 Jun;11(4):218-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00566.x. Epub 2008 Aug 25. Pediatr Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 19708904
-
Type 1 diabetes: current concepts in epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical care, and research.Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2012 Nov-Dec;42(10):269-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cppeds.2012.07.002. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2012. PMID: 23046732 Review.
-
Dysregulation of glucose metabolism in preclinical type 1 diabetes.Pediatr Diabetes. 2016 Jul;17 Suppl 22:25-30. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12392. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27411433 Review.
Cited by
-
Incident cardiovascular-kidney disease, diabetic ketoacidosis, hypoglycaemia and mortality in adult-onset type 1 diabetes: a population-based retrospective cohort study in Hong Kong.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023 Mar 16;34:100730. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100730. eCollection 2023 May. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023. PMID: 37283964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltesz G, Group ES. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989–2003 and predicted new cases 2005-20: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet. 2009;373(9680):2027–2033. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60568-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous