Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica transporters for high-efficient production of biobased succinic acid from glucose
- PMID: 34176501
- PMCID: PMC8237505
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-021-01996-w
Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica transporters for high-efficient production of biobased succinic acid from glucose
Abstract
Background: Succinic acid (SA) is a crucial metabolic intermediate and platform chemical. Development of biobased processes to achieve sustainable SA production has attracted more and more attention in biotechnology industry. Yarrowia lipolytica has a strong tricarboxylic acid cycle and tolerates low pH conditions, thus making it a potential platform for SA production. However, its SA titers in glucose media remain low.
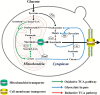
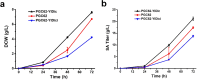
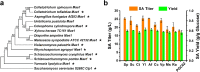
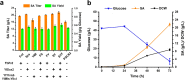
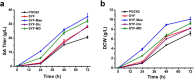
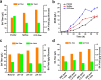
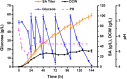
Results: In this study, we screened mitochondrial carriers and C4-dicarboxylic acid transporters to enhance SA secretion in Y. lipolytica. PGC62-SYF-Mae strain with efficient growth and SA production was constructed by optimizing SA biosynthetic pathways and expressing the transporter SpMae1. In fed-batch fermentation, this strain produced 101.4 g/L SA with a productivity of 0.70 g/L/h and a yield of 0.37 g/g glucose, which is the highest SA titer achieved using yeast, with glucose as the sole carbon resource.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that transporter engineering is a powerful strategy to achieve the efficient secretion of SA in Y. lipolytica, which will promote the industrial production of bio-based SA.
Keywords: Glucose fermentation; Succinic acid; Transporter engineering; Yarrowia lipolytica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Maziere A, Prinsen P, Garcia A, Luque R, Len C. A review of progress in (bio)catalytic routes from/to renewable succinic acid. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin. 2017;11:908–931. doi: 10.1002/bbb.1785. - DOI
-
- Puchalski M, Szparaga G, Biela T, Gutowska A, Sztajnowski S, Krucinska I. Molecular and supramolecular changes in polybutylene succinate (PBS) and polybutylene succinate adipate (PBSA) copolymer during degradation in various environmental conditions. Polymers. 2018;10(3):251. doi: 10.3390/polym10030251. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

