Preimplantation factor modulates trophoblastic invasion throughout the decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells
- PMID: 34176510
- PMCID: PMC8237507
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-021-00774-5
Preimplantation factor modulates trophoblastic invasion throughout the decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells
Abstract
Background: Successful human embryo implantation requires the differentiation of endometrial stromal cells (ESCs) into decidual cells during a process called decidualization. ESCs express specific markers of decidualization, including prolactin, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), and connexin-43. Decidual cells also control of trophoblast invasion by secreting various factors, such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Preimplantation factor (PIF) is a recently identified, embryo-derived peptide with activities at the fetal-maternal interface. It creates a favorable pro-inflammatory environment in human endometrium and directly controls placental development by increasing the human trophoblastic cells' ability to invade the endometrium. We hypothesized that PIF's effects on the endometrium counteract its pro-invasive effects.
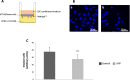
Methods: We tested sPIF effect on the expression of three decidualization markers by RT-qPCR and/or immunochemiluminescence assay. We examined sPIF effect on human ESC migration by performing an in vitro wound healing assay. We analyzed sPIF effect on endometrial control of human trophoblast invasion by performing a zymography and an invasion assay.
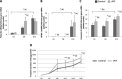
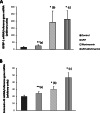
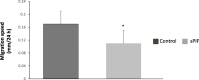
Results: Firstly, we found that a synthetic analog of PIF (sPIF) significantly upregulates the mRNA expression of IGFBP-1 and connexin-43, and prolactin secretion in ESCs - suggesting a pro-differentiation effect. Secondly, we showed that the HTR-8/SVneo trophoblastic cell line's invasive ability was low in the presence of conditioned media from ESCs cultured with sPIF. Thirdly, this PIF's anti-invasive action was associated with a specifically decrease in MMP-9 activity.
Conclusion: Taken as a whole, our results suggest that PIF accentuates the decidualization process and the production of endometrial factors that limit trophoblast invasion. By controlling both trophoblast and endometrial cells, PIF therefore appears to be a pivotal player in the human embryo implantation process.
Keywords: Decidualization; Embryo implantation; Human endometrium; Preimplantation factor (PIF); Signal transduction; Trophoblastic invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin limits differentiation and trophoblast invasion in human endometrial cells.J Mol Endocrinol. 2017 Oct;59(3):285-297. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0046. Epub 2017 Jul 21. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28733350
-
Invasiveness of human endometrial stromal cells is promoted by decidualization and by trophoblast-derived signals.Hum Reprod. 2010 Apr;25(4):862-73. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dep468. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Hum Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20118488
-
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II inhibition of endometrial stromal cell tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 and IGF-binding protein-1 suggests paracrine interactions at the decidua:trophoblast interface during human implantation.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001 May;86(5):2060-4. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.5.7451. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11344207
-
The motile and invasive capacity of human endometrial stromal cells: implications for normal and impaired reproductive function.Hum Reprod Update. 2013 Sep-Oct;19(5):542-57. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmt025. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Hum Reprod Update. 2013. PMID: 23827985 Review.
-
Decidualization of the human endometrial stromal cell: an enigmatic transformation.Reprod Biomed Online. 2003 Sep;7(2):151-61. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)61745-2. Reprod Biomed Online. 2003. PMID: 14567882 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk Between Trophoblast and Macrophage at the Maternal-Fetal Interface: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 21;12:758281. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.758281. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34745133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Microphysiological Model to Mimic the Placental Remodeling during Early Stage of Pregnancy under Hypoxia-Induced Trophoblast Invasion.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 May 12;9(5):289. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9050289. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786499 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional culture models of human endometrium for studying trophoblast-endometrium interaction during implantation.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022 Aug 13;20(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12958-022-00973-8. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35964080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decidual stromal cells-derived exosomes incured insufficient migration and invasion of trophoblast because of abnormal ubiquitination and degradation of Snail mediated by miR-92b-3p/USP28.BMC Biol. 2025 Jul 22;23(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02326-4. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40696416 Free PMC article.
-
Events Leading to the Establishment of Pregnancy and Placental Formation: The Need to Fine-Tune the Nomenclature on Pregnancy and Gestation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 21;24(20):15420. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015420. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

