Epigenetics of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a systematic review
- PMID: 34176557
- PMCID: PMC8726381
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.9514
Epigenetics of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a systematic review
Abstract
Study objectives: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a chronic and widely prevalent disease associated with multiple health disorders. Current diagnostic strategies for OSA are limited because of cost, time, and access. Epigenetic signatures offer insight into the relationships between disease and environment and could play a significant role in developing both diagnostic and therapeutic tools for OSA. In the current study, a systematic literature search was conducted to investigate the existing evidence of OSA-associated epigenetic modifications.
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed using electronic academic databases including PubMed, CINAHL, Scopus, Embase, EBM Reviews, and Web of Science. However, the current study focused on screening for original, English-language articles pertaining to OSA and associated epigenetic mechanisms. To produce unbiased results, screening was performed independently by authors.
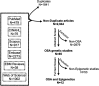
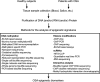
Results: We identified 2,944 publications in our systematic search. Among them, 65 research articles were related to OS A-associated differential gene expression, genetic variation, and epigenetic modifications. Although these 65 articles were considered for full manuscript review, only 12 articles met the criteria of OSA-associated epigenetic modifications in human and animal models. Human patients with OSA had unique epigenetic changes compared to healthy control patients and, interestingly, epigenetic signatures were commonly identified in genes associated with metabolic and inflammatory pathways.
Conclusions: Although the available studies are limited, this research provides novel insights for the development of epigenetic markers for the diagnosis and treatment of OSA. Thorough genome-wide investigations will be required to develop cost-effective, robust biomarkers for the identification of OSA among children and adults. Here, we offer a study design for such efforts.
Citation: Leader BA, Koritala BSC, Moore CA, Dean EG, Kottyan LC, Smith DF. Epigenetics of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a systematic review. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(12):2533-2541.
Keywords: biomarkers; epigenetics; obstructive sleep apnea; systematic review.
© 2021 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have seen and approved the manuscript. This study was funded by the Basic Research Grant from the American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology of the Combined Otolaryngology Research Effort, the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center Procter Scholar Award, and National Institutes of Health grant 5K08HL148551-02, all to DFS. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between socioeconomic status, belonging to an ethnic minority and obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review of the literature.Sleep Med. 2019 May;57:100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2019.01.042. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Sleep Med. 2019. PMID: 30954786
-
Circulating biomarkers to identify cardiometabolic complications in patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A systematic review.Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Apr;44:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 27. Sleep Med Rev. 2019. PMID: 30685729
-
Epigenetics modifications and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: The EPIOSA study.BMC Pulm Med. 2014 Jul 12;14:114. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-14-114. BMC Pulm Med. 2014. PMID: 25016368 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Forkhead Box P3 Methylation and Expression in Men with Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 23;21(6):2233. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062233. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32210181 Free PMC article.
-
Role of epigenetic abnormalities and intervention in obstructive sleep apnea target organs.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Mar 20;136(6):631-644. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002080. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 35245923 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the molecular and cellular links between obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome and vascular aging.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 Jan 20;138(2):155-171. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003352. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 39647991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of novel biomarkers in obstructive sleep apnea via integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.PeerJ. 2023 Dec 4;11:e16608. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16608. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38077447 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Pediatric Sleep Apnea.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 1;22(17):9523. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179523. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Importance of Sleep in Overcoming Childhood Obesity and Reshaping Epigenetics.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 15;12(6):1334. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061334. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
REM-OSA as a Tool to Understand Both the Architecture of Sleep and Pathogenesis of Sleep Apnea-Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 12;12(18):5907. doi: 10.3390/jcm12185907. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37762848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, et al. . American Academy of Pediatrics . Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome . Pediatrics. 2012. ; 130 ( 3 ): e714 – e755 . - PubMed
-
- Frost and Sullivan . Hidden health crisis costing America billions: underdiagnosing and undertreating obstructive sleep apnea draining healthcare system. Report for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Published 2016. . https://aasm.org/resources/pdf/sleep-apnea-economic-crisis.pdf. Accessed July 23, 2021.
-
- Parish JM, Somers VK . Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease . Mayo Clin Proc. 2004. ; 79 ( 8 ): 1036 – 1046 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

