Optofluidic Flow-Through Biosensor Sensitivity - Model and Experiment
- PMID: 34177078
- PMCID: PMC8224397
- DOI: 10.1109/jlt.2021.3061872
Optofluidic Flow-Through Biosensor Sensitivity - Model and Experiment
Abstract
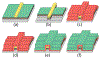
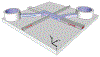
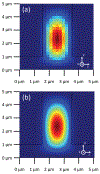
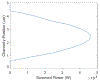
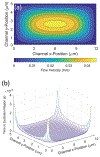
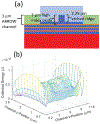
We present a model and simulation for predicting the detected signal of a fluorescence-based optical biosensor built from optofluidic waveguides. Typical applications include flow experiments to determine pathogen concentrations in a biological sample after tagging relevant DNA or RNA sequences. An overview of the biosensor geometry and fabrication processes is presented. The basis for the predictive model is also outlined. The model is then compared to experimental results for three different biosensor designs. The model is shown to have similar signal statistics as physical tests, illustrating utility as a pre-fabrication design tool and as a predictor of detection sensitivity.
Keywords: Anti-resonant reflecting optical waveguides (ARROW); integrated waveguides; model design; optofluidics; predictive simulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures A.R.H. and H.S. have a financial interest in Fluxus Inc., which commercializes optofluidic technology.
Figures
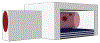
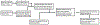






References
-
- Du K, Cai H, Wall TA, Stott MA, Alfson KJ, Griffiths A, Carrion R, Patterson JL, Hawkins AR, Schmidt H, and Mathies RA, “Multiplexed Efficient On-Chip Sample Preparation and Sensitive Amplification-Free Detection of Ebola Virus”, Biosens. Bioelectron, vol. 91, pp. 489–496, January. 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
