Identification of genes involved in Meloidogyne incognita-induced gall formation processes in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 34177318
- PMCID: PMC8215457
- DOI: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.20.0716a
Identification of genes involved in Meloidogyne incognita-induced gall formation processes in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
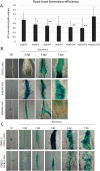
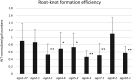
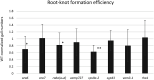
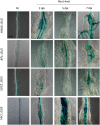
Root-knot nematodes (RKN; Meloidogyne incognita) are phytoparasitic nematodes that cause significant damage to crop plants worldwide. Recent studies have revealed that RKNs disrupt various physiological processes in host plant cells to induce gall formation. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of gall formation induced by nematodes. We have previously found that RNA expression levels of some of genes related to micro-RNA, cell division, membrane traffic, vascular formation, and meristem maintenance system were modified by nematode infection. Here we evaluated these genes importance during nematode infection by using Arabidopsis mutants and/or β-glucronidase (GUS) marker genes, particularly after inoculation with nematodes, to identify the genes involved in successful nematode infection. Our results provide new insights not only for the basic biology of plant-nematode interactions but also to improve nematode control in an agricultural setting.
Keywords: gall formation; plant–microorganism interaction; root-knot nematodes.
© 2021 Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology.
Figures

References
-
- Araki S, Ito M, Soyano T, Nishihama R, Machida Y (2004) Mitotic cyclins stimulate the activity of c-Myb-like factors for transactivation of G2/M phase-specific genes in tobacco. J Biol Chem 279: 32979–32988 - PubMed
-
- Asaoka R, Uemura T, Ito J, Fujimoto M, Ito E, Ueda T, Nakano A (2013) Arabidopsis RABA1 GTPases are involved in transport between the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane, and are required for salinity stress tolerance. Plant J 73: 240–249 - PubMed
-
- Bonke M, Thitamadee S, Mähönen AP, Hauser MT, Helariutta Y (2003) APL regulates vascular tissue identity in Arabidopsis. Nature 426: 181–186 - PubMed
-
- Burris RH, Roberts G (1993) Biological nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Nutr 13: 317–335 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
