In Silico and In Vivo Studies on the Mechanisms of Chinese Medicine Formula (Gegen Qinlian Decoction) in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
- PMID: 34177580
- PMCID: PMC8232523
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.665102
In Silico and In Vivo Studies on the Mechanisms of Chinese Medicine Formula (Gegen Qinlian Decoction) in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Abstract
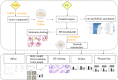
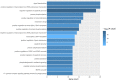
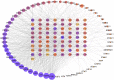
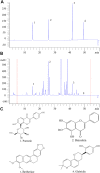
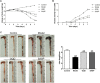
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and Gegen Qinlian Decoction (GQD), a Chinese botanical formula, has exhibited beneficial efficacy against UC. However, the mechanisms underlying the effect of GQD still remain to be elucidated. In this study, network pharmacology approach and molecular docking in silico were applied to uncover the potential multicomponent synergetic effect and molecular mechanisms. The targets of ingredients in GQD were obtained from Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP) and Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular mechANism of TCM (BATMAN-TCM) database, while the UC targets were retrieved from Genecards, therapeutic target database (TTD) and Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database. The topological parameters of Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) data were used to screen the hub targets in the network. The possible mechanisms were investigated with gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis. Molecular docking was used to verify the binding affinity between the active compounds and hub targets. Network pharmacology analysis successfully identified 77 candidate compounds and 56 potential targets. The targets were further mapped to 20 related pathways to construct a compound-target-pathway network and an integrated network of GQD treating UC. Among these pathways, PI3K-AKT, HIF-1, VEGF, Ras, and TNF signaling pathways may exert important effects in the treatment of UC via inflammation suppression and anti-carcinogenesis. In the animal experiment, treatment with GQD and sulfasalazine (SASP) both ameliorated inflammation in UC. The proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) induced by UC were significantly decreased by GQD and SASP. Moreover, the protein expression of EGFR, PI3K, and phosphorylation of AKT were reduced after GQD and SASP treatment, and there was no significance between the GQD group and SASP group. Our study systematically dissected the molecular mechanisms of GQD on the treatment of UC using network pharmacology, as well as uncovered the therapeutic effects of GQD against UC through ameliorating inflammation via downregulating EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and the pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6.
Keywords: gegen qinlian decoction (GQD); inflammatory bowel disease; molecular docking; network pharmacology; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Fan, Du, Mei and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


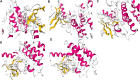

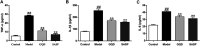

Similar articles
-
Deciphering the shared mechanisms of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in treating type 2 diabetes and ulcerative colitis via bioinformatics and machine learning.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 19;11:1406149. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1406149. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38962743 Free PMC article.
-
Based on Network Pharmacology to Explore the Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Gegen Qinlian Decoction for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 24;2020:5217405. doi: 10.1155/2020/5217405. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33299870 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Mechanisms of Self-made Kuiyu Pingchang Recipe for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis and Irritable Bowel Syndrome using a Network Pharmacology-based Approach and Molecular Docking.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(5):534-550. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230515103224. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37190808
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of the effect of Gegen Qinlian decoction on COVID-19 comorbid with diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 3;102(44):e34683. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034683. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37933071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational insights into the inhibitory mechanism of type 2 diabetes mellitus by bioactive components of Oryza sativa L. indica (black rice).Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 23;15:1457383. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1457383. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39380907 Free PMC article.
-
Active Ingredients and Potential Mechanisms of the Gan Jiang-Huang Qin-Huang Lian-Ren Shen Decoction against Ulcerative Colitis: A Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking-Based Study.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 8;2021:1925718. doi: 10.1155/2021/1925718. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34539797 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Mechanisms of Bisdemethoxycurcumin in Ulcerative Colitis: Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):68. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010068. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid Screening of Proanthocyanidins from the Roots of Ephedra sinica Stapf and its Preventative Effects on Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 10;12(10):957. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100957. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36295859 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific Evidence of Chinese Herbal Medicine (Gegen Qinlian Decoction) in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022 Mar 14;2022:7942845. doi: 10.1155/2022/7942845. eCollection 2022. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35356743 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

