Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction Ameliorates Pancreatic Fibrosis via JNK/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 34177589
- PMCID: PMC8223066
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.679557
Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction Ameliorates Pancreatic Fibrosis via JNK/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
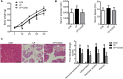
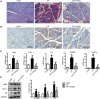
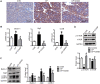
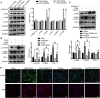
Pancreatic fibrosis is a pathological characteristic of chronic pancreatitis (CP) and pancreatic cancer. Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction (CGGD) is a traditional Chinese medicine, which is widely used in the clinical treatment of digestive diseases. However, the potential anti-fibrosis mechanism of CGGD in treating CP remains unclear. Here, we conducted a series of experiments to examine the effect of CGGD on the CP rat model and primary isolated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs). The results revealed that CGGD attenuated pancreatic damage, decreased collagen deposition, and inhibited PSC activation in the pancreas of CP rats. However, compared with the CP group, CGGD had no effect on body weight and serum amylase and lipase. In addition, CGGD suppressed autophagy by downregulating Atg5, Beclin-1, and LC3B and facilitated phosphorylation of mTOR and JNK in pancreatic tissues and PSCs. Moreover, the CGGD-containing serum also decreased LC3B or collagen I expression after rapamycin (mTOR inhibitor) or SP600125 (JNK inhibitor) treatment in PSCs. In conclusion, CGGD attenuated pancreatic fibrosis and PSC activation, possibly by suppressing autophagy of PSCs through the JNK/mTOR signaling pathway.
Keywords: Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction; JNK/mTOR; autophagy; chronic pancreatitis; pancreatic stellate cells.
Copyright © 2021 Cui, Li, Shang, Li, Zhuo, Yang, Cui, Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction ameliorates chronic pancreatitis by modulating the SK1/S1P signaling pathway.J Nat Med. 2025 May;79(3):706-720. doi: 10.1007/s11418-025-01901-x. Epub 2025 Apr 3. J Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 40178769
-
Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by enhancing intestinal barrier integrity and ameliorating PPARα mediated lipotoxicity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 23;326:117841. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117841. Epub 2024 Feb 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38310988
-
Chaihu-Guizhi-Ganjiang Decoction is more efficacious in treating irritable bowel syndrome than Dicetel according to metabolomics analysis.Chin Med. 2022 Dec 14;17(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00695-4. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36517857 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009 Nov;7(11 Suppl):S48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.07.038. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19896099 Review.
-
Pancreatic stellate cell: Pandora's box for pancreatic disease biology.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jan 21;23(3):382-405. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i3.382. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28210075 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Podocarpusflavone alleviated renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy by inhibiting Fyn/Stat3 signaling pathway.J Nat Med. 2023 Jun;77(3):464-475. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01685-y. Epub 2023 Mar 8. J Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 36884159
-
Pancreatic Stellate Cells and the Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Pancreatitis.Molecules. 2023 Jul 22;28(14):5586. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145586. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaiqin Chengqi Decoction as an adjuvant treatment for mild/moderately severe hypertriglyceridemic acute pancreatitis: A retrospective study.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Apr 16;12(11):1918-1928. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i11.1918. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38660541 Free PMC article.
-
Botanical drugs and their natural compounds: a neglected treasury for inhibiting the carcinogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):853-873. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2421759. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 39520705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in cellular senescence.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Aug;97(8):2089-2109. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03540-1. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37335314 Review.
References
-
- Chen F., Guo Y., Meng X., Zhang S. (1995). [Identification of Chaihu Guizhi Ganjiang Decoction by Three Dimensional HPLC]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 20 (4), 223–253. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

