Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System Loaded with Psiadia punctulata Major Metabolites for Hypertensive Emergencies: Effect on Hemodynamics and Cardiac Conductance
- PMID: 34177590
- PMCID: PMC8222910
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.681070
Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System Loaded with Psiadia punctulata Major Metabolites for Hypertensive Emergencies: Effect on Hemodynamics and Cardiac Conductance
Abstract
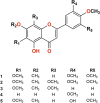
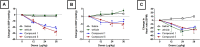
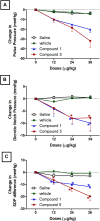
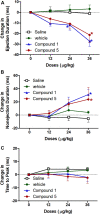
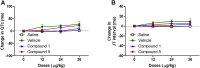
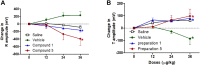
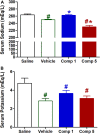
Vasodilators are an important class of antihypertensive agents. However, they have limited clinical use due to the reflex tachycardia associated with their use which masks most of its antihypertensive effect and raises cardiac risk. Chemical investigation of Psiadia punctulata afforded five major methoxylated flavonoids (1-5) three of which (1, 4, and 5) showed vasodilator activity. Linoleic acid-based self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) was utilized to develop intravenous (IV) formulations that contain compounds 1, 4, or 5. The antihypertensive effect of the prepared SNEDDS formulations, loaded with each of the vasodilator compounds, was tested in the angiotensin-induced rat model of hypertension. Rats were subjected to real-time recording of blood hemodynamics and surface Electrocardiogram (ECG) while the pharmaceutical formulations were individually slowly injected in cumulative doses. Among the tested formulations, only that contains umuhengerin (1) and 5,3'-dihydroxy-6,7,4',5'-tetramethoxyflavone (5) showed potent antihypertensive effects. Low IV doses, from the prepared SNEDDS, containing either compound 1 or 5 showed a marked reduction in the elevated systolic blood pressure by 10 mmHg at 12 μg/kg and by more than 20 mmHg at 36 μg/kg. The developed SNEDDS formulation containing either compound 1 or 5 significantly reduced the elevated diastolic, pulse pressure, dicrotic notch pressure, and the systolic-dicrotic notch pressure difference. Moreover, both formulations decreased the ejection duration and increased the non-ejection duration while they did not affect the time to peak. Both formulations did not affect the AV conduction as appear from the lack of effect on p duration and PR intervals. Similarly, they did not affect the ventricular repolarization as no effect on QTc or JT interval. Both formulations decreased the R wave amplitude but increased the T wave amplitude. In conclusion, the careful selection of linoleic acid for the development of SNEDDS formulation rescues the vasodilating effect of P. punctulata compounds from being masked by the reflex tachycardia that is commonly associated with the decrease in peripheral resistance by most vasodilators. The prepared SNEDDS formulation could be suggested as an effective medication in the treatment of hypertensive emergencies, after clinical evaluation.
Keywords: SNEDDS; methoxy flavonoids; reflex tachycardia; umuhengerin; vasodilators.
Copyright © 2021 Abdallah, El-Bassossy, El-Halawany, Ahmed, Mohamed, Malebari and Hassan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hinokitiol for hypertensive emergencies: effects on peripheral resistance, cardiac load, baroreflex sensitivity, and electrolytes balance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;396(6):1269-1277. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02400-0. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36710278 Free PMC article.
-
A Nano-Pharmaceutical Formula of Quercetin Protects from Cardiovascular Complications Associated with Metabolic Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 11;12:696981. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.696981. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34456723 Free PMC article.
-
Major flavonoids from Psiadia punctulata produce vasodilation via activation of endothelial dependent NO signaling.J Adv Res. 2020 Jan 3;24:273-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.01.002. eCollection 2020 Jul. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 32382447 Free PMC article.
-
Development of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems for the enhancement of solubility and oral bioavailability of fenofibrate, a poorly water-soluble drug.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Jun 14;11:2829-38. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S104187. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27366063 Free PMC article.
-
A Self-nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Poorly Water Soluble Tolbutamide: Development, Optimization and Pharmacodynamic Studies.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2017;5(4):285-300. doi: 10.2174/2211738505666170915154920. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28925888
Cited by
-
Hinokitiol for hypertensive emergencies: effects on peripheral resistance, cardiac load, baroreflex sensitivity, and electrolytes balance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;396(6):1269-1277. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02400-0. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36710278 Free PMC article.
-
Influences of Glimepiride Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System Loaded Liquisolid Tablets on the Hypoglycemic Activity and Pancreatic Histopathological Changes in Streptozotocin-Induced Hyperglycemic Rats.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;12(22):3966. doi: 10.3390/nano12223966. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432252 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Multi-Compartment 3D-Printed Tablets Loaded with Self-Nanoemulsified Formulations of Various Drugs: A New Strategy for Personalized Medicine.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 19;13(10):1733. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101733. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34684026 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolics from Chrozophora oblongifolia Aerial Parts as Inhibitors of α-Glucosidases and Advanced Glycation End Products: In-Vitro Assessment, Molecular Docking and Dynamics Studies.Biology (Basel). 2022 May 17;11(5):762. doi: 10.3390/biology11050762. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625490 Free PMC article.
-
Development of 3D-Printed, Liquisolid and Directly Compressed Glimepiride Tablets, Loaded with Black Seed Oil Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 5;15(1):68. doi: 10.3390/ph15010068. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achola K. J., Indalo A. A., Munenge R. W. (1998). Pharmacological Activities of Psiadia Punculata . Pharm. Biol. 36, 88–92. 10.1076/phbi.36.2.88.4605 - DOI
-
- Ahmed O. A. A., Badr-Eldin S. M., Tawfik M. K., Ahmed T. A., El-Say K. M., Badr J. M. (2014). Design and Optimization of Self-Nanoemulsifying Delivery System to Enhance Quercetin Hepatoprotective Activity in Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 103, 602–612. 10.1002/jps.23834 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

