Variation of Two S3b Residues in KV4.1-4.3 Channels Underlies Their Different Modulations by Spider Toxin κ-LhTx-1
- PMID: 34177600
- PMCID: PMC8222713
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.692076
Variation of Two S3b Residues in KV4.1-4.3 Channels Underlies Their Different Modulations by Spider Toxin κ-LhTx-1
Abstract
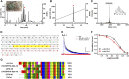
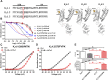
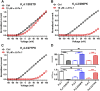
The naturally occurred peptide toxins from animal venoms are valuable pharmacological tools in exploring the structure-function relationships of ion channels. Herein we have identified the peptide toxin κ-LhTx-1 from the venom of spider Pandercetes sp (the Lichen huntsman spider) as a novel selective antagonist of the KV4 family potassium channels. κ-LhTx-1 is a gating-modifier toxin impeded KV4 channels' voltage sensor activation, and mutation analysis has confirmed its binding site on channels' S3b region. Interestingly, κ-LhTx-1 differently modulated the gating of KV4 channels, as revealed by toxin inhibiting KV4.2/4.3 with much more stronger voltage-dependence than that for KV4.1. We proposed that κ-LhTx-1 trapped the voltage sensor of KV4.1 in a much more stable resting state than that for KV4.2/4.3 and further explored the underlying mechanism. Swapping the non-conserved S3b segments between KV4.1(280FVPK283) and KV4.3(275VMTN278) fully reversed their voltage-dependence phenotypes in inhibition by κ-LhTx-1, and intensive mutation analysis has identified P282 in KV4.1, D281 in KV4.2 and N278 in KV4.3 being the key residues. Furthermore, the last two residues in this segment of each KV4 channel (P282/K283 in KV4.1, T280/D281 in KV4.2 and T277/N278 in KV4.3) likely worked synergistically as revealed by our combinatorial mutations analysis. The present study has clarified the molecular basis in KV4 channels for their different modulations by κ-LhTx-1, which have advanced our understanding on KV4 channels' structure features. Moreover, κ-LhTx-1 might be useful in developing anti-arrhythmic drugs given its high affinity, high selectivity and unique action mode in interacting with the KV4.2/4.3 channels.
Keywords: KV4 channels; anti-arrhythmic drugs; molecular basis; spider toxin; voltage-dependent inhibition.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao, Zhao, Wu, Kong, Wang, Liang, Tang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

