Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Possible Pathogenesis, and Management
- PMID: 34177799
- PMCID: PMC8224170
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.649863
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Possible Pathogenesis, and Management
Abstract
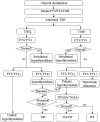
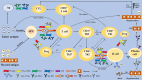
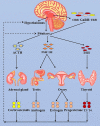
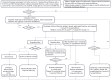
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are a group of drugs employed in the treatment of various types of malignant tumors and improve the therapeutic effect. ICIs blocks negative co-stimulatory molecules, such as programmed cell death gene-1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), reactivating the recognition and killing effect of the immune system on tumors. However, the reactivation of the immune system can also lead to the death of normal organs, tissues, and cells, eventually leading to immune-related adverse events (IRAEs). IRAEs involve various organs and tissues and also cause thyroid dysfunction. This article reviews the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, possible pathogenesis, and management of ICIs-related thyroid dysfunction.
Keywords: clinical manifestations; epidemiology; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune-related adverse events; management; pathogenesis; thyroid dysfunction.
Copyright © 2021 Zhan, Feng, Liu, Guo, Chen, Yao and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wu SP, Liao RQ, Tu HY, Wang WJ, Dong ZY, Huang SM, et al. . Stromal PD-L1-Positive Regulatory T Cells and PD-1-Positive CD8-Positive T Cells Define the Response of Different Subsets of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol (2018) 13(4):521–32. 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.11.132 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balatoni T, Mohos A, Papp E, Sebestyen T, Liszkay G, Olah J, et al. . Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells as Potential Biomarkers Predicting Response to Treatment and Survival in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma Receiving Ipilimumab Therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2018) 67(1):141–51. 10.1007/s00262-017-2072-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

