Protective Mechanism of Humanin Against Oxidative Stress in Aging-Related Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 34177809
- PMCID: PMC8222669
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.683151
Protective Mechanism of Humanin Against Oxidative Stress in Aging-Related Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
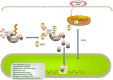
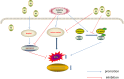
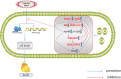
Physiological reactive oxygen species (ROS) are important regulators of intercellular signal transduction. Oxidative and antioxidation systems maintain a dynamic balance under physiological conditions. Increases in ROS levels destroy the dynamic balance, leading to oxidative stress damage. Oxidative stress is involved in the pathogenesis of aging-related cardiovascular diseases (ACVD), such as atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure, by contributing to apoptosis, hypertrophy, and fibrosis. Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria is the main source of ROS. Increasing evidence demonstrates the relationship between ACVD and humanin (HN), an endogenous peptide encoded by mitochondrial DNA. HN protects cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts from oxidative stress, highlighting its protective role in atherosclerosis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and heart failure. Herein, we reviewed the signaling pathways associated with the HN effects on redox signals, including Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), c-jun NH2 terminal kinase (JNK)/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)-Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Furthermore, we discussed the relationship among HN, redox signaling pathways, and ACVD. Finally, we propose that HN may be a candidate drug for ACVD.
Keywords: aging-related cardiovascular diseases; humanin; metabolic abnormalities; oxidative stress; redox signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2021 Cai, Liu, Men and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. . Global, Regional, and National Age-Sex-Specific Mortality for 282 Causes of Death in 195 Countries and Territories, 1980-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet (2018) 392:1736–88. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

