The Antimicrobial Peptide Mastoparan X Protects Against Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection, Inhibits Inflammation, and Enhances the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier
- PMID: 34177825
- PMCID: PMC8222680
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.644887
The Antimicrobial Peptide Mastoparan X Protects Against Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 Infection, Inhibits Inflammation, and Enhances the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier
Abstract
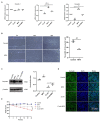
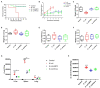
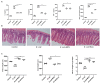
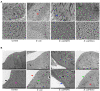
Escherichia coli can cause intestinal diseases in humans and livestock, destroy the intestinal barrier, exacerbate systemic inflammation, and seriously threaten human health and animal husbandry development. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the antimicrobial peptide mastoparan X (MPX) was effective against E. coli infection. BALB/c mice infected with E. coli by intraperitoneal injection, which represents a sepsis model. In this study, MPX exhibited no toxicity in IPEC-J2 cells and notably suppressed the levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), myeloperoxidase (MPO), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released by E. coli. In addition, MPX improved the expression of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin and enhanced the wound healing of IPEC-J2 cells. The therapeutic effect of MPX was evaluated in a murine model, revealing that it protected mice from lethal E. coli infection. Furthermore, MPX increased the length of villi and reduced the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the jejunum. SEM and TEM analyses showed that MPX effectively ameliorated the jejunum damage caused by E. coli and increased the number and length of microvilli. In addition, MPX decreased the expression of IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, p-p38, and p-p65 in the jejunum and colon. Moreover, MPX increased the expression of ZO-1, occludin, and MUC2 in the jejunum and colon, improved the function of the intestinal barrier, and promoted the absorption of nutrients. This study suggests that MPX is an effective therapeutic agent for E. coli infection and other intestinal diseases, laying the foundation for the development of new drugs for bacterial infections.
Keywords: Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7; antimicrobial peptide mastoparan X; inflammation; intestinal barrier; mice.
Copyright © 2021 Zhao, Wang, Zhu, Xia, Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Xu, Chen, Jiang, Liu, Wu, Wu, Zhang, Bai, Fotina and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral Administration of the Antimicrobial Peptide Mastoparan X Alleviates Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Inflammation and Regulates the Gut Microbiota.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Feb;16(1):138-151. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-10013-x. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 36515889
-
Lcn2 deficiency accelerates the infection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by disrupting the intestinal barrier function.Microb Pathog. 2023 Dec;185:106435. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106435. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Microb Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37931825
-
Human cathelicidin LL-37 exerts amelioration effects against EHEC O157:H7 infection regarding inflammation, enteric dysbacteriosis, and impairment of gut barrier function.Peptides. 2023 Jan;159:170903. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170903. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Peptides. 2023. PMID: 36370932
-
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of FST and its effects on inflammatory response and intestinal barrier function in mice infected with Escherichia coli O78.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Jan 25;127:111386. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111386. Epub 2023 Dec 17. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38109839
-
Protective Ability of Biogenic Antimicrobial Peptide Microcin J25 Against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli-Induced Intestinal Epithelial Dysfunction and Inflammatory Responses IPEC-J2 Cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jul 13;8:242. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00242. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30057893 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Iturin A Potentiates Differentiation of Intestinal Epithelial Defense Cells by Modulating Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling to Mitigate Oxidative Damage Induced by Heat-Stable Enterotoxin B.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;14(4):478. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040478. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298845 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of arginine replacement with L-citrulline on the arginine/nitric oxide metabolism in chickens: An animal model without urea cycle.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 1;14(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00817-w. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36721201 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides in Gut Health: A Review.Front Nutr. 2021 Sep 30;8:751010. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.751010. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34660671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CATH-2-derived antimicrobial peptide inhibits multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli infection in chickens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 15;14:1390934. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1390934. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38812753 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Administration of the Antimicrobial Peptide Mastoparan X Alleviates Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Inflammation and Regulates the Gut Microbiota.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Feb;16(1):138-151. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-10013-x. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 36515889
References
-
- Daneshmand A., Kermanshahi H., Sekhavati M. H., Javadmanesh A., Ahmadian M., Alizadeh M., et al. . (2020). Effects of cLFchimera peptide on intestinal morphology, integrity, microbiota, and immune cells in broiler chickens challenged with necrotic enteritis. Sci. Rep. 10:17704. 10.1038/s41598-020-74754-x, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

