Combined Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays for Rapid Detection and One-Step Differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Meat Products
- PMID: 34177847
- PMCID: PMC8219907
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.668824
Combined Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assays for Rapid Detection and One-Step Differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Meat Products
Abstract
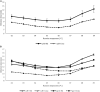
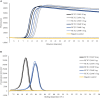
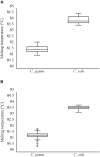
A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay system was established, allowing rplD gene-based simultaneous detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in enriched meat products. Additionally, one-step differentiation of target species on agar plates was enabled by cdtC gene- and gyrA gene-based duplex LAMP. Both the rplD and cdtC-gyrA LAMP assays amplified the target sequences in all 62 C. jejuni and 27 C. coli strains used for determining inclusivity and revealed 100% exclusivity toward 85 tested non-target species. Throughout the entire experiments, C. jejuni and C. coli strains were 100% distinguishable by melting curves of cdtC and gyrA LAMP products. After 24-h enrichment, the rplD LAMP assay reliably detected initial inoculation levels of 10-100 CFU/g in artificially contaminated minced meat. Investigation of naturally contaminated meat samples revealed a diagnostic accuracy of 95% toward real-time PCR and 94.1% toward the standard culture method applying the 24-h incubation period. Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were 89.8, 100, 100, and 91.2%, respectively, when measured against real-time PCR, and 89.6, 98.1, 97.7, and 91.2%, respectively, when measured against the standard culture method. After 48-h enrichment, the detection limit of the rplD LAMP assay improved to initial inoculation levels of 1-10 CFU/g in artificially contaminated minced meat. Applying the 48-h incubation period on naturally contaminated meat samples resulted in 100% concordant results between rplD LAMP, real-time PCR, and the standard culture method. The established LAMP assay system was proved to be suitable for rapid meat sample screening. Furthermore, it constitutes a promising tool for investigating other Campylobacter sources and could therefore make a valuable contribution to protect consumers from foodborne illness.
Keywords: Campylobacter; LAMP assay; cdtC gene; gyrA gene; meat products; rplD gene.
Copyright © 2021 Kreitlow, Becker, Ahmed, Kittler, Schotte, Plötz and Abdulmawjood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Cutoff Determination of Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for End-Point Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in Chicken Meat.Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 8;9(3):122. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9030122. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35324850 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay and conventional culture methods for detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in naturally contaminated chicken meat samples.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Mar;75(6):1597-603. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02004-08. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19139242 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid, sensitive detection of Campylobacter jejuni in cattle farm samples.J Food Prot. 2014 Sep;77(9):1593-8. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-056. J Food Prot. 2014. PMID: 25198853
-
Rapid and simultaneous detection of Campylobacter spp. and Salmonella spp. in chicken samples by duplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification coupled with a lateral flow biosensor assay.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 1;16(7):e0254029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254029. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34197563 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Detection Accuracy and Time for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Naturally Infected Live and Slaughtered Chicken Broilers Using a Real-Time Fluorescent Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Approach.J Food Prot. 2019 Feb;82(2):189-193. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-179. J Food Prot. 2019. PMID: 30702350
Cited by
-
Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid and direct screening of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) in commercial fish products.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 12;17(10):e0275452. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275452. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36223376 Free PMC article.
-
Immunocapture Magnetic Beads Enhanced the LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a Method for the Sensitive, Specific, and Visual Detection of Campylobacter jejuni.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;12(3):154. doi: 10.3390/bios12030154. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35323424 Free PMC article.
-
Quadruplex qPCR for detection and discrimination of C. Coli,C. fetus, and C. Jejuni from other Campylobacter species in chicken and sheep meat.Braz J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;55(3):2547-2556. doi: 10.1007/s42770-024-01437-4. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Braz J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38977544 Free PMC article.
-
A Cutoff Determination of Real-Time Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for End-Point Detection of Campylobacter jejuni in Chicken Meat.Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 8;9(3):122. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9030122. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35324850 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Diagnostic of Streptococcus suis in Necropsy Samples of Pigs by thrA-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 29;11(10):2447. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102447. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bundesamt für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit, (2013). “Untersuchung von Lebensmitteln - Nachweis von Campylobacter spp. in Hackfleisch - Real-time PCR-verfahren (BVL L 06.32-1:2013-08),” in Amtliche Sammlung von Untersuchungsverfahren nach §64 LFGB, ed. Band I. (Berlin: Beuth Verlag GmbH; ).
-
- Cagliero C., Mouline C., Cloeckaert A., Payot S. (2006). Synergy between efflux pump CmeABC and modifications in ribosomal proteins L4 and L22 in conferring macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50 3893–3896. 10.1128/aac.00616-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Devleesschauwer B., Bouwknegt M., Mangen M.-J. J., Havelaar A. H. (2017). “Health and economic burden of Campylobacter,” in Campylobacter, Chap. 2, ed. Klein G. (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; ), 27–40. 10.1016/b978-0-12-803623-5.00002-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

