A Homeodomain-Containing Transcriptional Factor Po Htf1 Regulated the Development and Cellulase Expression in Penicillium oxalicum
- PMID: 34177850
- PMCID: PMC8222722
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.671089
A Homeodomain-Containing Transcriptional Factor Po Htf1 Regulated the Development and Cellulase Expression in Penicillium oxalicum
Abstract
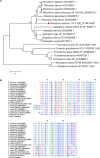
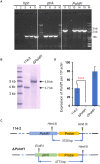
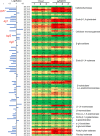
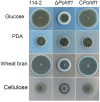
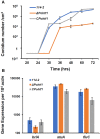
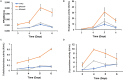
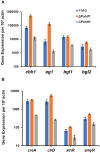
Homeodomain-containing transcription factors (Htfs) play important roles in animals, fungi, and plants during some developmental processes. Here, a homeodomain-containing transcription factor PoHtf1 was functionally characterized in the cellulase-producing fungi Penicillium oxalicum 114-2. PoHtf1 was shown to participate in colony growth and conidiation through regulating the expression of its downstream transcription factor BrlA, the key regulator of conidiation in P. oxalicum 114-2. Additionally, PoHtf1 inhibited the expression of the major cellulase genes by coordinated regulation of cellulolytic regulators CreA, AmyR, ClrB, and XlnR. Furthermore, transcriptome analysis showed that PoHtf1 participated in the secondary metabolism including the pathway synthesizing conidial yellow pigment. These data show that PoHtf1 mediates the complex transcriptional-regulatory network cascade between developmental processes and cellulolytic gene expression in P. oxalicum 114-2. Our results should assist the development of strategies for the metabolic engineering of mutants for applications in the enzymatic hydrolysis for biochemical production.
Keywords: Penicillium oxalicum; cellulase; conidiation; development; homeodomain-containing transcription factors.
Copyright © 2021 Guo, Xu, Wu, Li, Yan, Jia, Li, Chen, Bao and Qu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic and Dose-Controlled Regulation of Cellulase Gene Expression in Penicillium oxalicum.PLoS Genet. 2015 Sep 11;11(9):e1005509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005509. eCollection 2015 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26360497 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor NsdD Regulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Plant Biomass-Degrading Enzymes, Conidiation, and Pigment Biosynthesis in Penicillium oxalicum.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Aug 31;84(18):e01039-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01039-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29980558 Free PMC article.
-
The Different Roles of Penicillium oxalicum LaeA in the Production of Extracellular Cellulase and β-xylosidase.Front Microbiol. 2016 Dec 22;7:2091. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02091. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 28066400 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of cellulolytic enzyme production and performance by rational designing expression regulatory network and enzyme system composition.Bioresour Technol. 2017 Dec;245(Pt B):1718-1726. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.120. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Bioresour Technol. 2017. PMID: 28684177 Review.
-
Conservation and diversity of the regulators of cellulolytic enzyme genes in Ascomycete fungi.Curr Genet. 2017 Dec;63(6):951-958. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0695-6. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28451846 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Critical Environmental Optima and Biotechnological Prospects of Fungal Fruiting Bodies.Microb Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;18(8):e70210. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70210. Microb Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40810456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor FfMYB15 regulates the expression of cellulase gene FfCEL6B during mycelial growth of Flammulina filiformis.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Oct 17;21(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01932-z. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36253826 Free PMC article.
-
Phosducin-like protein PoPlp1 impacts cellulase and amylase expression and development in Penicillium oxalicum via the G protein-cAMP signaling pathway.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 9;14:1165701. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1165701. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37362916 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

