Evaluation of the brain hemodynamic response by means of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) monitoring in patients with atherosclerotic carotid disease undergoing endarterectomy
- PMID: 34178049
- PMCID: PMC8205114
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.190027
Evaluation of the brain hemodynamic response by means of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) monitoring in patients with atherosclerotic carotid disease undergoing endarterectomy
Abstract
Backgrounds: Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is non-invasive technique that detects hemodynamic alterations in tissues. It enables continuous monitoring of intracerebral vascular physiologic information. Due to its portable nature, NIRS may be used bedside or in the operating room.
Objectives: To evaluate use of NIRS for intraoperative monitoring of the brain hemodynamic response, during carotid endarterectomy.
Methods: 10 patients with atherosclerotic carotid disease scheduled for endarterectomy were evaluated. After patients had been selected, they answered a questionnaire on epidemiological data and information about comorbidities and then carotid disease was confirmed with diagnostic methods. NRIS monitoring was used during the surgical procedure. The variables analyzed before, during and after carotid clamping were oxygen saturation (SatO2), total hemoglobin (THb), reduced hemoglobin (RHb), and oxyhemoglobin (OHb). A p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
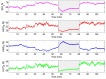
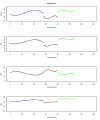
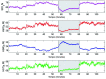
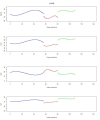
Results: The results obtained from NIRS show that RHb and SatO2 vary during the different stages of surgery. RHb levels are higher during clamping, when compared with the other two surgical stages. On the other hand, SatO2 is lower during clamping.
Conclusions: During carotid endarterectomy, NIRS is a feasible, real-time, and non-invasive intracranial monitoring method that accurately and reliably measures the changes in intracerebral capillary hemodynamic conditions.
Contexto: A espectroscopia próxima ao infravermelho (NIRS) é uma técnica não invasiva que detecta as alterações hemodinâmicas teciduais. A NIRS pode monitorar de forma contínua as informações fisiológicas vasculares intracranianas. Por ser portátil, ela pode ser utilizada à beira do leito e no centro cirúrgico.
Objetivos: Avaliar as possíveis alterações hemodinâmicas cerebrais durante a endarterectomia em pacientes com estenoses maiores que 70% utilizando NIRS.
Métodos: Foram avaliados 10 voluntários portadores de doença carotídea aterosclerótica com indicação de endarterectomia. Após a seleção dos pacientes, que responderam um questionário com dados epidemiológicos e informações referentes à presença de comorbidades, a doença foi confirmada por métodos diagnósticos. No procedimento cirúrgico, utilizou-se a NIRS para monitorização. Foram avaliadas as variáveis saturação de oxigênio (SatO2), hemoglobina total (HbT), hemoglobina reduzida (HbR) e hemoglobina oxigenada (HbO) nos três tempos cirúrgicos pré-, trans e pós-clampeamento carotídeo. Utilizou-se p < 0,05 como nível de significância.
Resultados: A avaliação dos resultados obtidos por meio das medidas registradas pela NIRS permite afirmar que HbR e SatO2 variam ao longo das etapas da cirurgia. Durante o clampeamento, a variável HbR mostra valores mais elevados que nas outras duas etapas da cirurgia. Por outro lado, a variável SatO2 mostra redução durante o clampeamento.
Conclusões: A NIRS é um método viável e aplicável de monitorização intracerebral, não invasivo e em tempo real, durante a endarterectomia carotídea, capaz de medir de forma precisa as mudanças das condições hemodinâmicas capilares intracerebrais.
Keywords: carotid artery disease; carotid endarterectomy; carotid stenosis; near-infrared spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No conflicts of interest declared concerning the publication of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Effect of Hemodynamic Parameters on Cerebral Oxygenization During Carotid Endarterectomy.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Mar 10;37(1):80-87. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0398. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 34236796 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of cerebral ischemia in neurovascular surgery using quantitative frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy.J Neurosurg. 2007 Feb;106(2):283-90. doi: 10.3171/jns.2007.106.2.283. J Neurosurg. 2007. PMID: 17410713 Clinical Trial.
-
The Diagnostic Accuracy of Intra-Operative Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Carotid Artery Endarterectomy Under Regional Anaesthesia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Oct;62(4):522-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.05.042. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34284934
-
Overview and Diagnostic Accuracy of Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Carotid Endarterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 Nov;62(5):695-704. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.08.022. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34627675
-
Defining thresholds for critical ischemia by using near-infrared spectroscopy in the adult brain.J Neurosurg. 1998 Sep;89(3):389-94. doi: 10.3171/jns.1998.89.3.0389. J Neurosurg. 1998. PMID: 9724112
References
-
- Becquemin JP, Alimi YS, Watelet J, Loisance D. Controversies and update in vascular and cardiac surgery. Torino, Italy: Edizioni Minerva Medica; 2004.
-
- Sloan MA. Prevention of ischemic neurologic injury with intraoperative monitoring of selected cardiovascular and cerebrovascular procedures: roles of electroencephalography, somatosensory evoked potentials, transcranial Doppler, and near-infrared spectroscopy. Neurol Clin. 2006;24(4):631–645. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2006.05.002. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
