Association between Silica Exposure and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34178083
- PMCID: PMC8217190
- DOI: 10.18502/jthc.v15i4.5940
Association between Silica Exposure and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
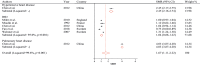
Background: Silica exposure is detrimental to health and has, thus, been a global health concern. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of existing articles to assess the involvement of silica exposure in cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality. Methods: Electronic databases including Web of Sciences, Scopus, PubMed, and Google Scholar were searched for eligible publication until December 2019. The pooled standard mortality ratio (SMR) and the 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to detect the association between silica exposure and CVD mortality. Results: The pooled estimates of SMR indicated a nonsignificant association between silica exposure and CVD mortality (SMR: 1.26; 95% CI: 0.88-1.63). The subgroup analysis based on the type of CVD indicated a significant positive association between silica exposure and mortality from hypertensive heart disease (SMR: 2.45; 95% CI: 2.16 -2.74) and pulmonary heart disease (SMR: 4.03; 95% CI: 3.87-4.20). Conclusion: This study confirmed that silica exposure is associated with an enhanced risk of mortality of hypertensive and pulmonary heart diseases. The verification of these results may have important effects on basic preventive strategies for health-care providers. Because of the mismatch in the silica exposure classification, some works in the literature were excluded. Also, the years of silica exposure may be important in CVD mortality. We suggest that these potential confounders be considered in future research.
Keywords: Angina pectoris; Cardiovascular diseases; Coronary artery disease; Silicosis.
Copyright © 2020 Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mortality from lung cancer among silicotic patients in Sardinia: an update study with 10 more years of follow up.Occup Environ Med. 2001 Dec;58(12):786-93. doi: 10.1136/oem.58.12.786. Occup Environ Med. 2001. PMID: 11706145 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Diagnosis and Suicide Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Arch Suicide Res. 2020;24(sup2):S94-S112. doi: 10.1080/13811118.2019.1596182. Epub 2019 May 9. Arch Suicide Res. 2020. PMID: 30955459
-
Occupational exposure to asbestos and cardiovascular related diseases: A meta-analysis.Prev Med Rep. 2015 Oct 21;2:920-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2015.10.005. eCollection 2015. Prev Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26844169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association Between Occupational Exposure to silica and Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis.Saf Health Work. 2020 Jun;11(2):136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.shaw.2020.02.001. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Saf Health Work. 2020. PMID: 32596007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystalline silica exposure, radiological silicosis, and lung cancer mortality in diatomaceous earth industry workers.Thorax. 1999 Jan;54(1):56-9. doi: 10.1136/thx.54.1.56. Thorax. 1999. PMID: 10343633 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Silica Exposure and Cardiovascular, Cerebrovascular, and Respiratory Morbidity in a Cohort of Male Swedish Iron Foundry Workers.J Occup Environ Med. 2023 Sep 1;65(9):731-739. doi: 10.1097/JOM.0000000000002890. Epub 2023 Jun 9. J Occup Environ Med. 2023. PMID: 37311079 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive Effects of Obesity and Hypertension on Patterns of Hair Essential Trace Element and Mineral Content in Adult Women.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Oct;201(10):4677-4687. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03561-y. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 36648598
References
-
- Cosselman KE, Navas-Acien A, Kaufman JD. Environmental factors in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12:627–642. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases. 2010. https://b2n.ir/900199.
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, Amann M, Anderson HR, Andrews KG, Aryee M, Atkinson C, Bacchus LJ, Bahalim AN, Balakrishnan K, Balmes J, Barker-Collo S, Baxter A, Bell ML, Blore JD, Blyth F, Bonner C, Borges G, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Brauer M, Brooks P, Bruce NG, Brunekreef B, Bryan-Hancock C, Bucello C, Buchbinder R, Bull F, Burnett RT, Byers TE, Calabria B, Carapetis J, Carnahan E, Chafe Z, Charlson F, Chen H, Chen JS, Cheng AT, Child JC, Cohen A, Colson KE, Cowie BC, Darby S, Darling S, Davis A, Degenhardt L, Dentener F, Des Jarlais DC, Devries K, Dherani M, Ding EL, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Edmond K, Ali SE, Engell RE, Erwin PJ, Fahimi S, Falder G, Farzadfar F, Ferrari A, Finucane MM, Flaxman S, Fowkes FG, Freedman G, Freeman MK, Gakidou E, Ghosh S, Giovannucci E, Gmel G, Graham K, Grainger R, Grant B, Gunnell D, Gutierrez HR, Hall W, Hoek HW, Hogan A, Hosgood HD 3rd, Hoy D, Hu H, Hubbell BJ, Hutchings SJ, Ibeanusi SE, Jacklyn GL, Jasrasaria R, Jonas JB, Kan H, Kanis JA, Kassebaum N, Kawakami N, Khang YH, Khatibzadeh S, Khoo JP, Kok C, Laden F, Lalloo R, Lan Q, Lathlean T, Leasher JL, Leigh J, Li Y, Lin JK, Lipshultz SE, London S, Lozano R, Lu Y, Mak J, Malekzadeh R, Mallinger L, Marcenes W, March L, Marks R, Martin R, McGale P, McGrath J, Mehta S, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Micha R, Michaud C, Mishra V, Mohd Hanafiah K, Mokdad AA, Morawska L, Mozaffarian D, Murphy T, Naghavi M, Neal B, Nelson PK, Nolla JM, Norman R, Olives C, Omer SB, Orchard J, Osborne R, Ostro B, Page A, Pandey KD, Parry CD, Passmore E, Patra J, Pearce N, Pelizzari PM, Petzold M, Phillips MR, Pope D, Pope CA 3rd, Powles J, Rao M, Razavi H, Rehfuess EA, Rehm JT, Ritz B, Rivara FP, Roberts T, Robinson C, Rodriguez-Portales JA, Romieu I, Room R, Rosenfeld LC, Roy A, Rushton L, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanchez-Riera L, Sanman E, Sapkota A, Seedat S, Shi P, Shield K, Shivakoti R, Singh GM, Sleet DA, Smith E, Smith KR, Stapelberg NJ, Steenland K, Stöckl H, Stovner LJ, Straif K, Straney L, Thurston GD, Tran JH, Van Dingenen R, van Donkelaar A, Veerman JL, Vijayakumar L, Weintraub R, Weissman MM, White RA, Whiteford H, Wiersma ST, Wilkinson JD, Williams HC, Williams W, Wilson N, Woolf AD, Yip P, Zielinski JM, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, Ezzati M, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guo J, Shi T, Cui X, Rong Y, Zhou T, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Shen Y, Chen W. Effects of silica exposure on the cardiac and renal inflammatory and fibrotic response and the antagonistic role of interleukin-1 beta in C57BL/6 mice. Arch Toxicol. 2016;90:247–258. - PubMed
-
- De Berardis B, Incocciati E, Massera S, Gargaro G, Paoletti L. Airborne silica levels in an urban area. Sci Total Environ. 2007;382:251–258. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
