A Comparative Study of the Methods to Assess Occupational Noise Exposures of Fish Harvesters
- PMID: 34178401
- PMCID: PMC8209409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.shaw.2020.10.005
A Comparative Study of the Methods to Assess Occupational Noise Exposures of Fish Harvesters
Abstract
Background: Noise-induced hearing loss is a well-known occupational disease that affects many fish harvesters from many fisheries worldwide, whose risk factor is prolonged exposure to hazardous noise levels. To date, academic research activities and regulatory bodies have not provided any comparative analysis among the existing methods to assess noise exposure levels of fish harvesters. This paper provides a comparison of four relevant assessment methods of noise exposure, examining the results of a measurement campaign performed onboard small fishing vessels from Newfoundland and Labrador.
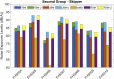
Methods: We traveled onboard 11 vessels engaged in multiple fisheries from Newfoundland and Labrador and performed extensive noise exposure surveys using the simplified International Maritime Organization method, the full-day measurement method, and the two methods provided by ISO 9612:2009, the task-based method and job-based method (JBM).
Results: The results showed that the four methods yield similar values when the noise components are dominated by the engine and auxiliaries (steady-state sources); when noise components are dominated by the fishing gear, task-based method and the simplified International Maritime Organization method estimates are less accurate than JBM, using full-day measurements as baseline.
Conclusion: The JBM better assesses noise exposure in small-scale fisheries, where noise exposure has significant variance and uncertainties on the exposure levels are higher.
Keywords: Fishing safety; Noise measurement methods; Occupational noise exposure; Risk assessment.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH); Cincinnati, OH: 1998. Criteria for a recommended standard–occupational noise exposure.
-
- Paini M.C., Morata T.C., Corteletti L.J., Albizu E., Marques J.M., Santos L. Audiological findings among workers from Brazilian small-scale fisheries. Ear Hear. 2009;30(1):8–15. - PubMed
-
- Levin J.L., Curry W.F., Shepherd S., Nalbone J.T., Nonnenmann M.W. Hearing loss and noise exposure among commercial fishermen in the gulf coast. J Occup Environ Med. 2016;58(3):306–313. - PubMed
-
- Kaerlev L., Jensen A., Nielsen P., Olsen J., Hannerz H., Tuchsen F. Hospital contacts for noise-related hearing loss among Danish seafarers and fishermen: a population-based cohort study. Noise Heal. 2009;10(39):41. - PubMed
-
- Novalbos J., Nogueroles P., Soriguer M., Piniella F. Occupational health in the andalusian fisheries sector. Occup Med (Chic Ill) 2008;58(2):141–143. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

