Factors Associated With Poor Long-Term Outcomes After Emergency Department Intubation
- PMID: 34178499
- PMCID: PMC8216642
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.15178
Factors Associated With Poor Long-Term Outcomes After Emergency Department Intubation
Abstract
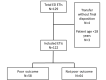
Introduction While immediate complications of ED patients undergoing endotracheal intubation (ETI) have been explored, the relationship between ED ETI and patient status at hospital discharge is unknown. Methods We performed a retrospective review of all intubations performed in our ED for one calendar year in adult patients (>18 years of age). We abstracted patient and ETI factors (indication, complications, etc.) to determine their impact on patient outcomes. We defined a poor outcome as either (1) death or discharge to a nursing home if admitted to the hospital from home or (2) death if admitted to the hospital from a nursing home. We examined the univariate odds ratios for poor outcomes. Results We identified 122 intubations; 64 (52.5%) had a poor outcome and 58 (47.5%) did not have a poor outcome. Age in years (odds ratio [OR] 1.04, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.02-1.07) and ETI performed for an indication of "cardiac arrest" (OR 4.49, 95% CI 1.55-13.01) were the only variables associated with a poor outcome. Other patients and intubation variables were not associated with a poor outcome including; gender, difficult airway characteristics, intubator skill level, first attempt success, airway complications, and post-intubation hypoxia or hypotension. Conclusion In our sample from a single ED, over 50% of patients who undergo ED ETI either died in the hospital or failed to return home. While age and an ETI indication of "cardiac arrest" were associated with poor outcomes, future work is required to validate our findings in a larger cohort.
Keywords: critical care; endotracheal intubation; hospital discharge; intubation; rsi; survival.
Copyright © 2021, Colleran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Incidence and factors associated with cardiac arrest complicating emergency airway management. Heffner AC, Swords DS, Neale MN, Jones AE. Resuscitation. 2013;84:1500–1504. - PubMed
-
- Characteristics and outcomes in adult patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a 28-day international study. Esteban A, Anzueto A, Frutos F, et al. JAMA. 2002;287:345–355. - PubMed
-
- Prolonged mechanical ventilation in 540 seriously ill older adults: effects of increasing age on clinical outcomes and survival. Dermot Frengley J, Sansone GR, Shakya K, Kaner RJ. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:1–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources