Gamma Ray Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Targeting Proximal or Distal to the Dorsal Root Entry Zone
- PMID: 34178514
- PMCID: PMC8218962
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.15194
Gamma Ray Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Targeting Proximal or Distal to the Dorsal Root Entry Zone
Abstract
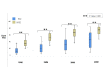
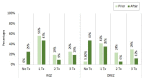
Introduction Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia (TN) has gained interest among patients who are not suitable for surgical procedures. Although two target zones are more recognized - dorsal root entry zone (DREZ) and retrogasserian zone (RGZ) - the optimal targeting technique remains controversial in terms of clinical outcomes and rates of complications. Therefore, various modifications to the radiosurgical technique for TN have been made. Objective This study aimed to determine the differences in shoot location (i.e., RGZ vs. DREZ) regarding effectiveness and adverse effects in patients with medically refractory TN. Additionally, we evaluated the effect of the integral dose (ID) on treatment outcomes and complications. Methods We present a retrospective cohort study of 49 patients with primary, drug-resistant TN treated with gamma knife radiosurgery targeting the distal and proximal parts of the nerve regarding the DREZ with a prescription dose of 90 Gy (80 to 96 Gy). A subset of these patients (n=38) where the ID could be measured to the nerve was correlated to treatment outcomes and complications. Results The median follow-up time was 36 months for RGZ and 51 months for DREZ targets. Neurovascular conflict was identified in 87.5% of the RGZ group and 88.2% of the DREZ group. Using the Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI) pain score, 26 (81.3%) RGZ and 12 (70.6%) DREZ patients were successfully treated (BNI I-IIIb; p=0.02). Seven (21.9%) RGZ and eight (47.1%) DREZ patients reported complete pain relief without medication (BNI I). Time response was 22.3 days for RGZ and 34.1 days for DREZ (p=0.277). There were 10 (31.3%) patients in the RGZ group with associated complications versus six (35.3%) patients in the DREZ group (χ2=0.0826, degree of freedom=1, p=0.773). Treatment outcomes using higher ID were better in the RGZ than DREZ (81.8% vs. 57.1, respectively), and a significant association was found between a higher ID delivered to the nerve and the development of complications (p=0.02). Conclusion Based on the obtained results, the RGZ was a more effective targeting area with better treatment outcomes without significant differences in complication rates than DREZ. A higher ID at the RGZ than DREZ had a greater therapeutical effect. Further investigation regarding the optimal target area along the ID delivered and clinical outcomes are required.
Keywords: gamma knife (gk) radiosurgery; intracranial radiosurgery; secondary trigeminal neuralgia; stereotactic and functional neurosurgery; trigeminal nerve.
Copyright © 2021, Lovo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radiosurgery target location and individual anatomical variation in trigeminal nerves.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121 Suppl:203-9. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.GKS141432. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25434954
-
LINAC stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia -retrospective two-institutional examination of treatment outcomes.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Aug 22;13(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1102-2. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30134992 Free PMC article.
-
The retrogasserian zone versus dorsal root entry zone: comparison of two targeting techniques of gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010 Jul;152(7):1165-70. doi: 10.1007/s00701-010-0610-0. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010. PMID: 20204664
-
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by a Cavernous Malformation: Case Report and Literature Review.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2018;96(6):412-415. doi: 10.1159/000495476. Epub 2019 Jan 16. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30650431 Review.
-
Optimizing Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Impact of Radiation Dose and Anatomic Target on Patient Outcomes.World Neurosurg. 2020 Nov;143:e482-e491. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.206. Epub 2020 Aug 3. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32758651
Cited by
-
Radioneuromodulation by Dual-Target Irradiation in Pain Crisis From Trigeminal Neuralgia.Cureus. 2022 Jan 5;14(1):e20971. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20971. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35004092 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Target Radiosurgery for Concomitant Continuous Pain Presentation of Trigeminal Neuralgia: Radiomodulation Effect and Dose.Cureus. 2024 Jan 3;16(1):e51602. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51602. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38313895 Free PMC article.
-
Trigeminal neuralgia.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024 May 30;10(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00523-z. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024. PMID: 38816415 Review.
-
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Vertebrobasilar Compression: A Report of Four Cases.Cureus. 2024 Jan 24;16(1):e52880. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52880. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38406158 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes and predictive factors after second stereotactic radiosurgery for refractory trigeminal neuralgia.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2025 Apr 29;53:100969. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2025.100969. eCollection 2025 Jul. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40485909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. Tuleasca C, Régis J, Sahgal A, et al. J Neurosurg. 2018;130:733–757. - PubMed
-
- Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: first case series from Latin America. Constanzo F, Silva RSD, de Almeida DB, Ferragut MA, Coelho Neto M, Toledo HV, Ramina R. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2019;77:232–238. - PubMed
-
- Prevalence of trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review. De Toledo IP, Conti Réus J, Fernandes M, et al. J Am Dent Assoc. 2016;147:570–576. - PubMed
-
- Radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: the state of art. Marchetti M, Pinzi V, De Martin E, Ghielmetti F, Fariselli L. Neurol Sci. 2019;40:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Prospective comparison of posterior fossa exploration and stereotactic radiosurgery dorsal root entry zone target as primary surgery for patients with idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Pollock BE, Schoeberl KA. Neurosurgery. 2010;67:633–638. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
