Effects of Grief Focused Intervention on the Mental Health of Dementia Caregivers: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34178734
- PMCID: PMC8215047
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v49i12.4808
Effects of Grief Focused Intervention on the Mental Health of Dementia Caregivers: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The objectives of this study were to review systematically the effects of grief-focused interventions, applied to dementia caregivers, on emotional burden including sadness and to provide baseline information for dementia caregivers to maintain mental health by identifying the effect size of intervention using a meta-analysis.
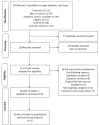
Methods: We evaluated literature published from Jan 1, 2000, to Jun 28, 2019. Consequently, we selected five studies to conduct a systematic review. The Standard Quality Assessment Criteria for Evaluating Primary Research Papers from a Variety of Fields was used for conducting a quality assessment on the selected literature.
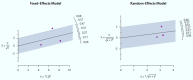
Results: The results of the quality assessment showed that the score ranged from 11 to 24 points: one strong, one good, two adequate, and one limited. When the meta-mean was compared before and after grief intervention, the effect size of the random-effect model was 0.31 (95% CI: -0.07, 0.69) showed 'intermediate effect', but the confidence interval was not significant.
Conclusion: The grief intervention for dementia caregivers revealed a moderate effect but it was not significant. In order to prove the effectiveness of grief intervention for dementia caregivers, a meta-analysis targeting RCT studies is needed.
Keywords: Dementia caregivers; Grief intervention; Meta-analysis; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2020 Byeon. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
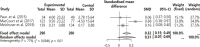
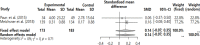

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of interventions that assist caregivers to support people with dementia living in the community: a systematic review.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008 Jun;6(2):137-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2008.00090.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008. PMID: 21631819
-
Effectiveness of interventions that assist caregivers to support people with dementia living in the community: a systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2008;6(13):484-544. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200806130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 27820474
-
Remotely delivered information, training and support for informal caregivers of people with dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 4;1(1):CD006440. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006440.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33417236 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of psychosocial interventions on the psychological health and emotional well-being of family carers of people with dementia following residential care placement: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018 May;16(5):1240-1268. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003634. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018. PMID: 29762315
-
"Easing the way" for spouse caregivers of individuals with dementia: a pilot feasibility study of a grief intervention.Res Gerontol Nurs. 2010 Apr;3(2):89-99. doi: 10.3928/19404921-20100302-01. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Res Gerontol Nurs. 2010. PMID: 20415358 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Grief, bereavement and prolonged grief disorder: scoping and mapping the evidence.BJPsych Open. 2025 Jul 11;11(4):e149. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2025.10050. BJPsych Open. 2025. PMID: 40641083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International (2015). World Alzheimer’s Report 2015. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International. United Kingdom.
-
- Ministry of Health and Welfare (2013). 2012 survey of dementia prevalence. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea.
-
- Korea National Statistical Office (2016). The causes of death statistics in 2015. Daejeon: Korea National Statistical Office. Korea.
-
- Dunkin JJ, Anderson-Hanley C. (1998). Dementia caregiver burden: a review of the literature and guidelines for assessment and intervention. Neurology, 51(1 Suppl 1):S53–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
