Comparison of the Therapeutic Effects of Sodium Valproate and Levetiracetam on Pediatric Epilepsy and the Effects of Nerve Growth Factor and γ-Aminobutyric Acid
- PMID: 34178799
- PMCID: PMC8214608
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v50i3.5593
Comparison of the Therapeutic Effects of Sodium Valproate and Levetiracetam on Pediatric Epilepsy and the Effects of Nerve Growth Factor and γ-Aminobutyric Acid
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the therapeutic effect of sodium valproate combined with levetiracetam on pediatric epilepsy and the effects of nerve growth factor and γ-aminobutyric acid.
Methods: Eighty-three epileptic children admitted to Xuzhou Municipal Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University (Xuzhou, China) from Jan 2018 to Nov 2019 were collected and divided into a control group (40 cases, treated with sodium valproate alone) and an observation group (43 cases, treated with sodium valproate combined with levetiracetam). The therapeutic effect and incidence of adverse reactions were observed. The levels of nerve growth factor (NGF), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and serum neuron-specific enolase (NSE) of children were compared. Changes of cognitive function and the total effective rate were evaluated. Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the risk factors affecting the therapeutic effect.
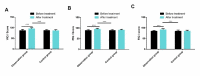
Results: After treatment, NGF, GABA and NSE in the observation group were significantly improved compared with those before treatment. The cognitive function of the observation group was significantly improved after treatment when compared with the control group. The total effective rate in the observation group was higher than that in the control group. Adverse reactions in the observation group were less than those in the control group. Seizure type, NGF, GABA, NSE and treatment methods were independent risk factors affecting the therapeutic effect of pediatric epilepsy.
Conclusion: The application of sodium valproate combined with levetiracetam in the treatment of pediatric epilepsy is helpful to improve the overall therapeutic effect, significantly improve the cognitive function of children, and improve the levels of NGF, GABA and NSE.
Keywords: Gamma-aminobutyric acid; Levetiracetam; Nerve growth factor; Pediatric epilepsy; Sodium valproate.
Copyright © 2021 Chen et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sodium valproate combined with levetiracetam in pediatric epilepsy and its influence on NSE, IL-6, hs-CRP and electroencephalogram improvement.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2043-2048. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8916. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32782515 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of sodium valproate plus lamotrigine in children with refractory epilepsy.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2698-2704. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8984. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32765764 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of levetiracetam combined with sodium valproate on pediatric epilepsy and its effect on serum miR-106b in children.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4436-4442. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8098. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31777547 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy in Patients of Child-Bearing Potential.CNS Drugs. 2019 Mar;33(3):195-208. doi: 10.1007/s40263-018-00602-2. CNS Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30747367 Review.
-
Ethosuximide, sodium valproate or lamotrigine for absence seizures in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Feb 8;2(2):CD003032. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003032.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 21;1:CD003032. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003032.pub5. PMID: 30734919 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Levetiracetam Versus Sodium Valproate as a Monotherapy in Early Childhood Epilepsy.Cureus. 2025 Jul 9;17(7):e87574. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87574. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40786292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korsholm K, Ian L. (2013). Effects of a ketogenic diet on brain metabolism in epilepsy. Clin Nucl Med 38 (1): 38–9. - PubMed
-
- Kumkamthornkul P, Udnaen S, Tansit T, et al. (2018). Evaluation of a lymphocyte transformation test and cytokine detection assay to identify phenytoin and carbamazepine provoked DRESS or SJS/TEN in epilepsy patients. Int Immunopharmacol, 63: 204–210. - PubMed
-
- Hauser WA. (1995). Epidemiology of epilepsy in children. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 6(3):419–29. - PubMed
-
- Dwivedi R, Ramanujam B, Chandra P S, et al. (2017). Surgery for drug-resistant epilepsy in children. N Engl J Med, 377: 1639–1647. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
