The Association between Serum Oxidative Stress Indexes and Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease in the Northwest of Iran
- PMID: 34178809
- PMCID: PMC8214605
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v50i3.5621
The Association between Serum Oxidative Stress Indexes and Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease in the Northwest of Iran
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder. Oxidative stress is a main modulator in the advancement of PD. This investigation aimed to evaluate the relations between serum trace elements, vitamin C, ferritin, transferrin, Nitrite Oxide (NOx) and Peroxynitrite (PrN) concentrations and clinical parameters in patients with PD.
Methods: Serum concentrations of variables were measured in 75 PD patients and 75 healthy subjects from Imam Reza Hospital, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran between Feb 2016 and Sep 2018. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to examine incremental diagnostic value of vitamin C, NOx, and PrN in the study groups.
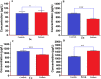
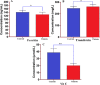
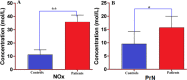
Results: Mean serum NOx (35.81±5.16 vs. 11.27±3.59 mol/L, P<0.001) and PrN (15.78±4.23 vs. 9.62±4.57 mol/L, P= 0.004) were markedly higher in patient group versus healthy individuals. Significant differences were also observed in the serum levels of vitamin C (P<0.001), copper (Cu) (P<0.001), Iron (Fe) (P=0.003), and Zinc (Zn) (P<0.001) between patients with PD and healthy subjects. Nevertheless, the serum levels of Se (P=0.515), ferritin (P=0.103), and transferrin (P=0.372) were not statistically significant between the study groups. ROC analysis has revealed a diagnostic ability of serum vitamin C levels for PD with an area under ROC curve of ≥0.7 (P<0.05) and relatively high sensitivity and specificity.
Conclusion: Serum levels of NOx and PrN are significantly higher in patients with PD. In additions, serum vitamin C levels have a diagnostic value as a biomarker. Further studies are required with larger sample size to provide more detailed information about the cognitive profile of participants and the outcome measures.
Keywords: Ferritin; Nitric oxide; Oxidative stress; Parkinson diseases; Trace elements.
Copyright © 2021 Barmaki et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hemmati-Dinarvand M, Taher-Aghdam A-A, Mota A, Vahed SZ, Samadi N. (2017). Dysregulation of serum NADPH oxidase1 and ferritin levels provides insights into diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Biochem, 50(18):1087–1092. - PubMed
-
- Kouti L, Noroozian M, Akhondzadeh S, et al. (2013). Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite serum levels in Parkinson’s disease: correlation of oxidative stress and the severity of the disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 17(7):964–70. - PubMed
-
- Wang N, Jin X, Guo D, Tong G, Zhu X. (2017). Iron chelation nanoparticles with delayed saturation as an effective therapy for Parkinson Disease. Biomacromolecules, 18(2):461–474. - PubMed
-
- Prasad S, Gupta SC, Tyagi AK. (2017). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cancer: Role of antioxidative nutraceuticals. Cancer Lett, 387:95–105. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
