Effect of yoga on glycemia and lipid parameters in type-2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 34178843
- PMCID: PMC8212260
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00751-0
Effect of yoga on glycemia and lipid parameters in type-2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Prior systematic reviews on yoga and diabetes have given conflicting results. They have been limited by inclusion of uncontrolled unblinded single group observational studies. No reviews are available which have used the Cochrane methodology and GRADE (Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach. This meta-analysis evaluated the efficacy of yoga on glycaemia and lipids in T2DM using the Cochrane methodology and GRADE approach.
Methods: Major repositories were searched to pick randomized controlled trials involving T2DM patients receiving yoga. Primary outcome was to evaluate changes in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c). Secondary outcomes were to evaluate changes in post-prandial plasma glucose (PPG), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Sub-group analysis involving people undergoing structured exercise regimen (SER) versus those undergoing standard diabetes care in controls was done.
Results: Data from 13 studies involving 1440 patients were analysed. Compared to controls, individuals doing yoga had significantly lower FPG [mean difference (MD) -17.22 mg/dl (95% CI: -26.19 - -8.26 mg/dl); p < 0.01; considerable heterogeneity (CH); low certainty of evidence (LCE)], PPG [MD -27.77 mg/dl (95% CI: -35.73 - -19.81 mg/dl); p < 0.01; low heterogeneity; moderate certainty of evidence (MCE)], TC [MD -19.48 mg/dl (95% CI: -31.97 - -6.99 mg/dl); p < 0.01; CH; LCE], triglycerides [MD -12.99 mg/dl (95% CI: -23.74 - -2.25 mg/dl); p < 0.01; CH; LCE], LDL-C [MD -11.71 mg/dl (95% CI: -17.49 - -5.93 mg/dl); p < 0.01; I2 = 69% CH; LCE] and significantly higher HDL-C [MD 4.58 mg/dl (95% CI: 3.98-5.18 mg/dl); p < 0.01; low heterogeneity; MCE]. On sub-group analysis, where yoga was compared to SER, FPG was significantly lower in yoga group.
Conclusion: Yoga improves glycaemia and lipid parameters in T2DM with additional benefits seen both in people doing/not doing structured exercise.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40200-021-00751-0.
Keywords: Diabetes; Exercise; Meta-analysis; Yoga.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestsDD, SB, MS, DK, VS and SK have no conflict of interests with regard to this research work and have nothing to declare.
Figures
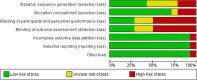
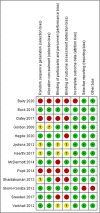

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of saroglitazar in managing hypertriglyceridemia in type-2 diabetes: A meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Nov-Dec;14(6):1759-1768. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.039. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32937280
-
Effect of Pilates on Glucose and Lipids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Physiol. 2021 May 28;12:641968. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.641968. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34135767 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of yoga in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis.J Diabetes Investig. 2017 Mar;8(2):201-209. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12548. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Diabetes Investig. 2017. PMID: 27370357 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of Huanglian Wendan decoction in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 6;102(40):e35299. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035299. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37800822 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of Coptis chinensis Franch.-containing traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunct therapy to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 8;13:956313. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.956313. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160405 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of yoga for arterial hypertension.PLoS One. 2025 May 14;20(5):e0323268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323268. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40367243 Free PMC article.
-
ADA-EASD Consensus Report on the Management of Hyperglycaemia in Type 2 Diabetes in an Afro-Asian Context: Broadening the Perspective.touchREV Endocrinol. 2023 Nov;19(2):4-6. doi: 10.17925/EE.2023.19.2.1. Epub 2023 Apr 21. touchREV Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 38187081 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of 24-Week Yoga Intervention on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Inflammatory Markers in Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Yoga. 2023 Jan-Apr;16(1):27-33. doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_176_22. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Int J Yoga. 2023. PMID: 37583542 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the benefits of yoga for myositis, muscle dystrophies, and other musculoskeletal disorders.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Nov;41(11):3285-3297. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06280-2. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35854165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of yoga therapy directed by virtual training on depression of adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Jul 1;22(2):1273-1281. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01245-x. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 37975133 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

