Propolis ethanol extract abrogates hyperglycemia, lipotoxicity, and lowered hepatic poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase protein level in male albino rats
- PMID: 34178859
- PMCID: PMC8212341
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00800-8
Propolis ethanol extract abrogates hyperglycemia, lipotoxicity, and lowered hepatic poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase protein level in male albino rats
Abstract
Background and aim: Diabetes is a major cause of death worldwide and currently available allopathic drugs presents adverse side effects, thus, necessitating a continuous screening for natural products. This study therefore investigated the effects of Propolis Ethanol Extract (PEE) on blood sugar, lipid metabolism, and poly-(ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARPs) protein level of diabetic male Wistar rats.
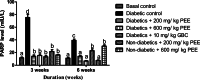
Methodology: Seventy rats weighing between (150-180) g used in this study were randomized into seven (7) groups as follows: group 1 (Normal control given Olive oil), group 2 (Diabetic control given Olive oil), group 3 [Diabetic + PEE (200 mg/kg)], group 4 [Diabetic + (PEE 600 mg/kg)], group 5 [Diabetic + Glibenclamide (10 mg/kg)], group 6 [Normal + PEE (200 mg/kg)], and group 7 [Normal + PEE (600 mg/kg)]. Diabetes was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (65 mg/kg in 0.1 M citrate buffer pH 4.5), while the vehicle and PEE were orally administered once daily. Treatment with PEE commenced after the confirmation of diabetes. Five rats from each group were sacrificed after the third and sixth weeks of PEE treatment.
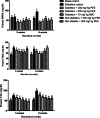
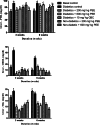
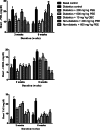
Results: Administration of PEE significantly (P < 0.05) lowered the elevated fasting blood sugar, improves body weight, and abated lipotoxicity in the brain, heart, liver and kidney of the treated groups in a dose- and duration-dependent manners. The increased protein level of PARPs and lowered hydroxyl methyl-glutaryl CoA reductase activity were significantly reversed after PEE treatment.
Conclusions: This study concludes that PEE might be a suitable and viable regimen against diabetic complications in rats.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Diabetes; Hyperglycemia; Hyperlipidemia; PARPs; Propolis.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestWe declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Brazilian propolis ethanol extract and its component kaempferol induce myeloid-derived suppressor cells from macrophages of mice in vivo and in vitro.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 2;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2198-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29720160 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal ethanol exposure programs an increased susceptibility of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in female adult offspring rats.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 15;274(2):263-73. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.11.009. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24275070
-
Potential therapeutic effect of Moroccan propolis in hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hepatorenal dysfunction in diabetic rats.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Nov;22(11):1331-1339. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.33549.8004. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32128099 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoprotection by propolis ethanol extract of acute absolute ethanol-induced gastric mucosal lesions.Am J Chin Med. 2002;30(2-3):245-54. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X02000387. Am J Chin Med. 2002. PMID: 12230013
-
Protective effect of propolis ethanol extract on ethanol-induced renal toxicity: an in-vivo study.Am J Chin Med. 2005;33(5):779-86. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X05003363. Am J Chin Med. 2005. PMID: 16265990
Cited by
-
Propolis: An update on its chemistry and pharmacological applications.Chin Med. 2022 Aug 26;17(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00651-2. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36028892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Malini P, Kanchana G, Rajadurai MU. Antibiabetic efficacy of ellagic acid in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in albino Wistar rats. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2011;4(3):124–8.
-
- Stryer L. Biochemistry, editors. New York: W. H. Freeman and company; 2000; pp. 779–780.
-
- Shankarprasad DS, Gundalli S, Mahantesh B, Kashinakunti SV, Sunitha P. Lipid profile in diabetes mellitus. Indian J Pathol Oncol. 2015;2(4):290–4. doi: 10.5958/2394-6792.2015.00030.7. - DOI
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Mathews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetes Spectr. 2012;25(3):154–71. doi: 10.2337/diaspect.25.3.154. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chattanda SP, Mgonda YM. Diabetic dyslipidemia among diabetic patients attending specialized clinics in Dar es Salaam. Tanzan Med J. 2008;23(1):8–11. doi: 10.4314/tmj.v23i1.39221. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

