Low to no cost remedies for the management of diabetes mellitus; global health concern
- PMID: 34178869
- PMCID: PMC8212264
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00783-6
Low to no cost remedies for the management of diabetes mellitus; global health concern
Abstract
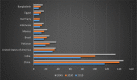
Purpose: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic non-communicable endocrine and metabolic disease that is thought to be the fastest emerging health challenge of the twenty-first century. Presently, 90% of diabetic population is handicapped with T2-DM, and the majority of pre-diabetes on the way to T2-DM progression. By keeping in view, a review article has been compiled to highlight the significance of value aided effective, low-cost, safe, and useful remedies that could easily be accessible to the global community in order to moderate the possibility of DM and related complications.
Methods: Literature search for this review was carried out using scientific databases including PubMed, EBSCO, Scopus, Web of science, and google scholar. Whilst, value aided articles were selected on the basis of their therapeutic potential, safety profile and outreach.
Results: Escalating research data validated that herbal remedies and physical activities significantly prevents hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and other complications in people with T2-DM.
Conclusion: Globally, nearly half-billion individuals are living with diabetes. Therefore, it is urged to embrace herbal remedies and physical mediation in our daily routine in order to tackle such devastating disorder.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Global public health; Kitchen herbs, herbal beverages; Physical therapies; T2-DM.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthor is declaring no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanoformulation of Plant-Based Natural Products for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: From Formulation Design to Therapeutic Applications.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2022 Apr 21;96:100672. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2022.100672. eCollection 2022. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2022. PMID: 35586563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The burden of Diabetes, Its Oral Complications and Their Prevention and Management.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Aug 15;6(8):1545-1553. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.294. eCollection 2018 Aug 20. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30159091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common Ayurvedic, Chinese traditional and Unani antidiabetic formulations- a review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 12;13:991083. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.991083. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost of illness of diabetes mellitus in Indonesia: a systematic review.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 25;32(4):285-295. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2020-0502. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34214313
-
Comparative occurrence of diabetes in canine, feline, and few wild animals and their association with pancreatic diseases and ketoacidosis with therapeutic approach.Vet World. 2018 Apr;11(4):410-422. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.410-422. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Vet World. 2018. PMID: 29805204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GC-MS Analysis and Biomedical Therapy of Oil from n-Hexane Fraction of Scutellaria edelbergii Rech. f.: In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Silico Approach.Molecules. 2021 Dec 18;26(24):7676. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247676. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946757 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effects of Vitamin D and Exercise on Diabetes-induced Gonadotoxicity in Male Wistar Rats: Role of Xanthine Oxidase/Uric Acid and Nrf2/NfkB Signaling.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):2065-2077. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01313-w. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38831172
-
Synergistic Effects of Nigella sativa and Exercise on Diabetic Profiles: A Systematic Review.Diabetes Ther. 2023 Mar;14(3):467-478. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01362-5. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Diabetes Ther. 2023. PMID: 36645572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Scoping Review of the Clinical Evidence for the Health Benefits of Culinary Doses of Herbs and Spices for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 22;15(23):4867. doi: 10.3390/nu15234867. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38068725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Worldwide toll of diabetes. Diabetesatlas.org. 2020. https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/sections/worldwide-toll-of-diabetes.html. Accessed 7 Aug 2020.
-
- Deyno S, Eneyew K, Seyfe S, Tuyiringire N, Peter EL, Muluye RA, Tolo CU, Ogwang PE. Efficacy and safety of cinnamon in type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes patients: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;156:107815. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107815. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

