Health Measurement Model-Bringing a Life Course Perspective to Health Measurement: The PRISM Model
- PMID: 34178878
- PMCID: PMC8222802
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.605932
Health Measurement Model-Bringing a Life Course Perspective to Health Measurement: The PRISM Model
Abstract
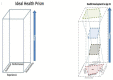
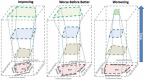
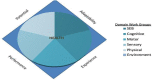
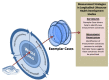
Health is a multidimensional concept that is challenging to measure, and in the rapidly evolving developmental changes that occur during the first 21 years of human life, requires a dynamic approach to accurately capture the transitions, and overall arc of a complex process of internal and external interactions. We propose an approach that integrates a lifecourse framework with a layered series of assessments, each layer using a many to many mapping, to converge on four fundamental dimensions of health measurement-Potential, Adaptability, Performance, and Experience. The four dimensions can conceptually be mapped onto a plane with each edge of the resulting quadrilateral corresponding to one dimension and each dimensions assessment calibrated against a theoretical ideal. As the plane evolves over time, the sequential measurements will form a volume. We term such a model the Prism Model, and describe conceptually how single domain assessments can be built up to generate the holistic description through the vehicle of a layer of Exemplar Cases. The model is theoretical but future work can use the framework and principles to generate scalable and adaptable applications that can unify and improve the precision of serial measurements that integrate environmental and physiologic influences to improve the science of child health measurement.
Keywords: childhood; health measurement; life course health development; longitudinal study; measurement models.
Copyright © 2021 Hirschfeld, Goodman, Barkin, Faustman, Halfon and Riley.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Right care, first time: a highly personalised and measurement-based care model to manage youth mental health.Med J Aust. 2019 Nov;211 Suppl 9:S3-S46. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50383. Med J Aust. 2019. PMID: 31679171
-
Risk management frameworks for human health and environmental risks.J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003 Nov-Dec;6(6):569-720. doi: 10.1080/10937400390208608. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev. 2003. PMID: 14698953 Review.
-
A qualitative systematic review of internal and external influences on shared decision-making in all health care settings.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(58):4633-4646. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-432. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820528
-
The life mission theory VII. Theory of existential (Antonovsky) coherence: a theory of quality of life, health, and ability for use in holistic medicine.ScientificWorldJournal. 2005 May 6;5:377-89. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2005.47. ScientificWorldJournal. 2005. PMID: 15915291 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and evaluation of developed and used health scores.Health Promot Int. 2023 Apr 1;38(2):daad005. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daad005. Health Promot Int. 2023. PMID: 37029770
Cited by
-
Designing a Visit Schedule for Longitudinal Studies in Pediatric Research.Front Pediatr. 2022 Sep 12;10:883994. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.883994. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36172389 Free PMC article.
-
Improving child health through Big Data and data science.Pediatr Res. 2023 Jan;93(2):342-349. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02264-9. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 35974162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Principles of Researching Health Disparities in Longitudinal Cohort Studies Enrolling Children.Front Pediatr. 2021 Nov 19;9:627298. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.627298. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34869088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paradoxes in pediatric rehabilitation: building an interdisciplinary, total-child framework to promote effective interventions and life course well-being.Front Pediatr. 2025 Mar 10;13:1540479. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1540479. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40129700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bronfenbrenner U. Ecology of the family as a context for human development: research perspectives. Dev Psychol. (1986) 22:723–42. 10.1037/0012-1649.22.6.723 - DOI
-
- Bronfenbrenner U, Morris PA. The Bioecological Model of Human Development. Handbook of Child Psychology. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (2007). 10.1002/9780470147658.chpsy0114 - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . Human Development Index. (1990).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

