Current Biological Strategies to Enhance Surgical Treatment for Rotator Cuff Repair
- PMID: 34178957
- PMCID: PMC8226184
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.657584
Current Biological Strategies to Enhance Surgical Treatment for Rotator Cuff Repair
Abstract
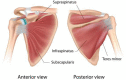
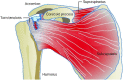
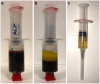
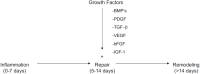
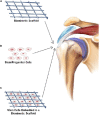
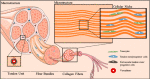
Rotator cuff tear is one of the most common shoulder problems encountered by orthopedic surgeons. Due to the slow healing process and high retear rate, rotator cuff tear has distressed millions of people all around the world every year, especially for the elderly and active athletes. This disease significantly impairs patients' motor ability and reduces their quality of life. Besides conservative treatment, open and arthroscopic surgery contributes a lot to accelerate the healing process of rotator cuff tear. Currently, there are many emerging novel treatment methods to promote rotator cuff repair. A variety of biological stimulus has been utilized in clinical practice. Among them, platelet-rich plasma, growth factors, stem cells, and exosomes are the most popular biologics in laboratory research and clinical trials. This review will focus on the biologics of bioaugmentation methods for rotator cuff repair and tendon healing, including platelet-rich plasma, growth factors, exosomes and stem cells, etc. Relevant studies are summarized in this review and future research perspectives are introduced.
Keywords: exosomes; growth factor; platelet-rich plasma; rotator cuff repair; stem cell; tendon healing.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Wu, Li, Wang, Lu and Wong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on rotator cuff tendon healing: a prospective, randomized clinical study.Am J Sports Med. 2012 Jun;40(6):1234-41. doi: 10.1177/0363546512442924. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Am J Sports Med. 2012. PMID: 22495146 Clinical Trial.
-
Does platelet-rich plasma accelerate recovery after rotator cuff repair? A prospective cohort study.Am J Sports Med. 2011 Oct;39(10):2082-90. doi: 10.1177/0363546511413454. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Am J Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 21737832 Clinical Trial.
-
[Progress and prospect of biological treatment for rotator cuff injury repair].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Sep 15;37(9):1169-1176. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202303122. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37718433 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes promote rotator cuff tendon-bone healing.Injury. 2024 Feb;55(2):111212. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2023.111212. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Injury. 2024. PMID: 37984013
-
Biological strategies to enhance rotator cuff healing.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013 Nov;8(6):464-70. doi: 10.2174/1574888x113086660065. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24059330 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Effects of 630 nm Wavelength of Light-Emitting Diode Irradiation on the Proliferation and Migration Ability of Human Biceps Tendon Fibroblast Cells.Clin Orthop Surg. 2023 Feb;15(1):166-174. doi: 10.4055/cios22132. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Surg. 2023. PMID: 36779000 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopic therapy of rotator cuff diseases: A bibliometric study of the past 2 decades (2002-2021).Front Surg. 2022 Sep 15;9:927638. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.927638. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36189396 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes in Soft Tissue Repair and Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3869. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073869. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue-engineered Bicipital Autologous Tendon Patch Enhances Massive Rotator Cuff Defect Repair in a Rabbit Infraspinatus Tendon Defect Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2239-2255. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003218. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39467146
-
Effect of Decellularized Amniotic Membrane on the Tendon-Bone Integration in Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparative Rat Model Study.Orthop Surg. 2025 Feb;17(2):575-582. doi: 10.1111/os.14316. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 39660410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Bakr E., Abu-Ahmed H., Elblehi S., El-Kammar M., Abdelwahed R. (2020). Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) vs propolis for cutaneous equine wound healing. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 64 69–75. 10.5455/ajvs.67207 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

