Coupling of Cell Surface Biotinylation and SILAC-Based Quantitative Proteomics Identified Myoferlin as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis
- PMID: 34178975
- PMCID: PMC8219959
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.621810
Coupling of Cell Surface Biotinylation and SILAC-Based Quantitative Proteomics Identified Myoferlin as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Metastasis
Abstract
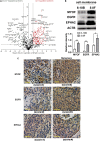
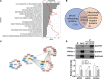
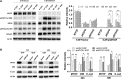
Distant metastasis is a major cause of treatment failure in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients. Cell surface proteins represent attractive targets for cancer diagnosis or therapy. However, the cell surface proteins associated with NPC metastasis are poorly understood. To identify potential therapeutic targets for NPC metastasis, we isolated cell surface proteins from two isogenic NPC cell lines, 6-10B (low metastatic) and 5-8F (highly metastatic), through cell surface biotinylation. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) based proteomics was applied to comprehensively characterize the cell surface proteins related with the metastatic phenotype. We identified 294 differentially expressed cell surface proteins, including the most upregulated protein myoferlin (MYOF), two receptor tyrosine kinases(RTKs) epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EPHA2) and several integrin family molecules. These differentially expressed proteins are enriched in multiple biological pathways such as the FAK-PI3K-mTOR pathway, focal adhesions, and integrin-mediated cell adhesion. The knockdown of MYOF effectively suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of NPC cells. Immunohistochemistry analysis also showed that MYOF is associated with NPC metastasis. We experimentally confirmed, for the first time, that MYOF can interact with EGFR and EPHA2. Moreover, MYOF knockdown could influence not only EGFR activity and its downstream epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), but also EPHA2 ligand-independent activity. These findings suggest that MYOF might be an attractive potential therapeutic target that has double effects of simultaneously influencing EGFR and EPHA2 signaling pathway. In conclusion, this is the first study to profile the cell surface proteins associated with NPC metastasis and provide valuable resource for future researches.
Keywords: SILAC; biotinylation; cell surface proteins; metastasis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Peng, Wang, Liang, Shao, Chen and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
S897 phosphorylation of EphA2 is indispensable for EphA2-dependent nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell invasion, metastasis and stem properties.Cancer Lett. 2019 Mar 1;444:162-174. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30583071
-
Along with its favorable prognostic role, CLCA2 inhibits growth and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via inhibition of FAK/ERK signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 20;37(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0692-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29463274 Free PMC article.
-
c-Src activation promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis by inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: a new and promising target for NPC.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28340-55. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8634. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27078847 Free PMC article.
-
Lectin affinity chromatography and quantitative proteomic analysis reveal that galectin-3 is associated with metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 5;10(1):16462. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73498-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33020562 Free PMC article.
-
H19/miR-675-5p Targeting SFN Enhances the Invasion and Metastasis of Nasalpharyngeal Cancer Cells.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019;12(4):324-333. doi: 10.2174/1874467212666190719120446. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31677258
Cited by
-
Mass spectrometry-based methods for investigating the dynamics and organization of the surfaceome: exploring potential clinical implications.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2024 Jan-Mar;21(1-3):99-113. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2024.2314148. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38300624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 ligase TRIM8 suppresses lung cancer metastasis by targeting MYOF degradation through K48-linked polyubiquitination.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Feb 11;16(1):88. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07421-6. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 39934162 Free PMC article.
-
Biotin conjugates in targeted drug delivery: is it mediated by a biotin transporter, a yet to be identified receptor, or (an)other unknown mechanism(s)?J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2276663. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2276663. Epub 2023 Nov 13. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37955285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular characteristics and prognostic role of EPHA2 in human tumors via pan-cancer analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 29;103(48):e40741. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040741. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39612413 Free PMC article.
-
Myoferlin disturbs redox equilibrium to accelerate gastric cancer migration.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 6;12:905230. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.905230. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36147922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartolomé R. A., García-Palmero I., Torres S., López-Lucendo M., Balyasnikova I. V., Casal J. I. (2015). IL13 receptor alpha2 signaling requires a scaffold protein, FAM120A, to activate the FAK and PI3K pathways in colon cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 75 2434–2444. 10.1158/0008-5472.can-14-3650 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cao S. M., Yang Q., Guo L., Mai H. Q., Mo H. Y., Cao K. J., et al. (2017). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a phase III multicentre randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Cancer 75 14–23. 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.12.039 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

