Dual Characters of GH-IGF1 Signaling Pathways in Radiotherapy and Post-radiotherapy Repair of Cancers
- PMID: 34178997
- PMCID: PMC8220142
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.671247
Dual Characters of GH-IGF1 Signaling Pathways in Radiotherapy and Post-radiotherapy Repair of Cancers
Abstract
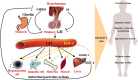
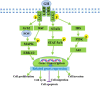
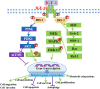
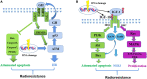
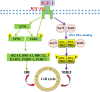
Radiotherapy remains one of the most important cancer treatment modalities. In the course of radiotherapy for tumor treatment, the incidental irradiation of adjacent tissues could not be completely avoided. DNA damage is one of the main factors of cell death caused by ionizing radiation, including single-strand (SSBs) and double-strand breaks (DSBs). The growth hormone-Insulin-like growth factor 1 (GH-IGF1) axis plays numerous roles in various systems by promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis, supporting its effects in inducing the development of multiple cancers. Meanwhile, the GH-IGF1 signaling involved in DNA damage response (DDR) and DNA damage repair determines the radio-resistance of cancer cells subjected to radiotherapy and repair of adjacent tissues damaged by radiotherapy. In the present review, we firstly summarized the studies on GH-IGF1 signaling in the development of cancers. Then we discussed the adverse effect of GH-IGF1 signaling in radiotherapy to cancer cells and the favorable impact of GH-IGF1 signaling on radiation damage repair to adjacent tissues after irradiation. This review further summarized recent advances on research into the molecular mechanism of GH-IGF1 signaling pathway in these effects, expecting to specify the dual characters of GH-IGF1 signaling pathways in radiotherapy and post-radiotherapy repair of cancers, subsequently providing theoretical basis of their roles in increasing radiation sensitivity during cancer radiotherapy and repairing damage after radiotherapy.
Keywords: DNA damage repair; GH-IGF1 signaling pathway; cancers; radio-resistance; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 Cheng, Li, Gui, Wang, Song, Wang, Wang, Shen, Wang and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The intrahepatic biliary epithelium is a target of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis.J Hepatol. 2005 Nov;43(5):875-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.04.011. Epub 2005 May 31. J Hepatol. 2005. PMID: 16083987
-
Role of the GH-IGF1 system in progression of cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Dec 1;518:111003. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.111003. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32919021 Review.
-
Exploiting DNA repair pathways for tumor sensitization, mitigation of resistance, and normal tissue protection in radiotherapy.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021;4(2):244-263. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.89. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34337349 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone regulation of follicular growth.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2011;24(1):19-28. doi: 10.1071/RD11903. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2011. PMID: 22394714 Review.
-
Circadian aspects of growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis function in patients with lung cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2012 Jan;13(1):68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2011.03.034. Epub 2011 May 19. Clin Lung Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21729653
Cited by
-
TRIP13 protects pancreatic cancer cells against intrinsic and therapy-induced DNA replication stress.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2025.01.26.634889. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.26.634889. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: NAR Cancer. 2025 Mar 20;7(1):zcaf009. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcaf009. PMID: 39975297 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
TRIP13 protects pancreatic cancer cells against intrinsic and therapy-induced DNA replication stress.NAR Cancer. 2025 Mar 20;7(1):zcaf009. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcaf009. eCollection 2025 Mar. NAR Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40115747 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone and radiation therapy: friend, foe, or both?Endocr Relat Cancer. 2024 Jan 24;31(3):e220371. doi: 10.1530/ERC-22-0371. Print 2024 Mar 1. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38174978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

