Green Synthesis of Highly Dispersed Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Supported on Silica Gel Matrix by Daphne oleoides Extract and their Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 34179191
- PMCID: PMC8217538
- DOI: 10.30498/IJB.2021.2598
Green Synthesis of Highly Dispersed Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Supported on Silica Gel Matrix by Daphne oleoides Extract and their Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
Background: ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are one of the most popular metal oxide nanoparticles, which exhibit significant antibacterial properties against various pathogens. Among nanoparticle synthesis methods, the green synthesis using plant extract is considered as an eco-friendly and cost-effective method for ZnO-NPs production, compared to the chemical procedures.
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the green synthesis of ZnO-NPs loaded on silica gel matrix (ZnO/SG nanocomposite) by using methanol leaf extract of Daphne oleoides as a new extract and a cost-effective method. Furthermore, the antibacterial activity of the synthesized structure is evaluated against some pathogenic bacteria and the results are compared with unsupported ZnO-NPs.
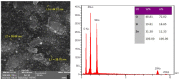
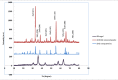
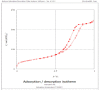
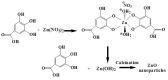
Materials and methods: For ZnO/SG nanocomposite synthesis, a solution of Zn (NO3)2 was stirred with silica gel. Then the Daphne oleoides extract was added and stirred continuously until white precipitate was formed. The precipitate was heated at 200 ˚C for calcination, and ZnO/SG nanocomposite was obtained. The phytochemical constituents of leaf extract were then analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Afterwards, the structure of ZnO-NPs on SiO2 matrix (ZnO/SG nanocomposite) was characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Surface area measurement was also determined by Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) techniques. Furthermore, the antibacterial activity of ZnO/SG nanocomposites against pathogenic bacteria was evaluated using agar-based disk diffusion method standardized by clinical and laboratory guidelines.
Results: The leaf extract of Daphne oleoides encompassed five major polyphenolic components. The results of the nanocomposite structure showed that ZnO-NPs with an average particle size of 38 nm were obtained and stabilized on the silica gel matrix. The BET surface area measurement of ZnO/SG nanocomposite was compared with unsupported ZnO-NPs, and the results indicated that the surface area of ZnO/SG nanocomposite was increased. Furthermore, the structure showed more powerful antibacterial activity against pathogens than unsupported ZnO-NPs.
Conclusions: Green synthesis of ZnO-NPs supported on the silica gel matrix with the leaf extract of Daphne oleoides is a benign and effective procedure for ZnO/SG nanocomposite synthesis. Embedding ZnO-NPs in silica gel matrix prevents the agglomeration of nanoparticles and prepare homodispersed nanoparticles. This structure revealed great antibacterial activity against many pathogens.
Keywords: Antibacterial Activity; Daphne oleoides extract; Green chemistry; Silica gel; ZnO Nanoparticles.
Copyright: © 2021 The Author(s); Published by Iranian Journal of Biotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None .
Figures
Similar articles
-
Green Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Pelargonium odoratissimum (L.) Aqueous Leaf Extract and Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1444. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081444. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892646 Free PMC article.
-
Green Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Phlomis Leaf Extract: Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Properties.Molecules. 2021 Oct 11;26(20):6140. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206140. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684721 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using a Dysphania ambrosioides extract. Structural characterization and antibacterial properties.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Jan;118:111540. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111540. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 33255092
-
Exploring the Journey of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) toward Biomedical Applications.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;15(6):2160. doi: 10.3390/ma15062160. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35329610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Plant-Mediated ZnO Nanoparticles for Photodegradation and Antibacterial Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jul 11;14(14):1182. doi: 10.3390/nano14141182. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesis of Polylactic acid/Fe3O4@β-Cyclodextrin Nanofibrous Nanocomposite Loaded with Ferulago Angulata Extract as a Novel Nano-biosorbent: Evaluation of Diazinon Removal and Antibacterial Activity.Iran J Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 1;21(4):e3682. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2023.392864.3682. eCollection 2023 Oct. Iran J Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38269202 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Based Bimetallic Silver-Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Perspective of Synthesis, Biomedical Applications, and Future Trends.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 30;2022:1215183. doi: 10.1155/2022/1215183. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35535038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications - A Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 3;19:12889-12937. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S487188. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39651353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rogers MA. Naturally occurring nanoparticles in food. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2016;7:14–19. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2015.08.005. - DOI
-
- Das DK, Sarkar J. Theoretical calculation of atomic and physical properties of some low-dimensional nanomaterials. Mater Today-Proc. 2018; 5(14, Part 2):27982–27988. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.10.038. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
