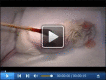
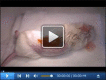
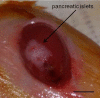
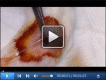
Murine Pancreatic Islets Transplantation under the Kidney Capsule
- PMID: 34179271
- PMCID: PMC8203884
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2743
Murine Pancreatic Islets Transplantation under the Kidney Capsule
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease caused by the lack of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells leading to systemic hyperglycemia. Pancreatic islet transplantation is a valid therapeutic approach to restore insulin loss and to promote adequate glycemic control. Pancreatic islet transplantation in mice is an optimal preclinical model to identify new therapeutic strategies aiming at preventing rejection and optimizing post-transplant immuno-suppressive/-tolerogenic therapies. Islet transplantation in preclinical animal models can be performed in different sites such the kidney capsule, spleen, bone marrow and pancreas. This protocol describes murine islet transplantation under the kidney capsule. This is a widely accepted procedure for research purposes. Stress caused in the animals is minimal and it leads to reliable and reproducible results.
Keywords: Islet transplantation; Murine model; Pancreatic islets; Type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures
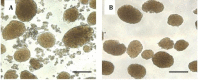
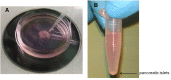
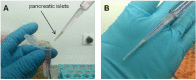
References
-
- Andersson A.(1978). Isolated mouse pancreatic islets in culture: effects of serum and different culture media on the insulin production of the islets . Diabetologia 14(6): 397-404. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia M., Stabilini A., Draghici E., Gregori S., Mocchetti C., Bonifacio E. and Roncarolo M. G.(2006). Rapamycin and interleukin-10 treatment induces T regulatory type 1 cells that mediate antigen-specific transplantation tolerance. Diabetes 55(1): 40-49. - PubMed
-
- Cantarelli E. and Piemonti L.(2011). Alternative transplantation sites for pancreatic islet grafts. Curr Diab Rep 11(5): 364-374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

