Preclinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Coptidis Preparation in Combination with Lovastatin in High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats
- PMID: 34179624
- PMCID: PMC8223438
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01201
Preclinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Coptidis Preparation in Combination with Lovastatin in High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats
Abstract
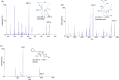
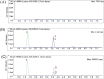
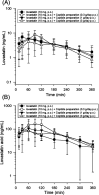
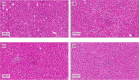
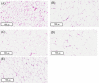
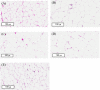
Lovastatin is a standard therapy for dyslipidemia. Alternatively, some ethnomedicines, such as Coptidis preparation, have been used for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Statins and complementary and alternative medicines may possess individual mechanisms of action against dyslipidemia. We hypothesize that the combination of Coptidis preparation and lovastatin may have synergistic effects for the treatment of dyslipidemia. To investigate this hypothesis, we developed a validated ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method to monitor lovastatin and its metabolites for pharmacokinetic studies in rats. This study was divided into four groups: lovastatin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) alone and lovastatin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) + Coptidis preparation (0.3, 1, or 3 g/kg, p.o.) for five consecutive days. In pharmacodynamic studies, a high-fat diet (HFD) was used to induce dyslipidemia in experimental rat models. The HFD rats were divided into four groups: treatment with HFD, HFD + lovastatin (100 mg/kg, p.o.), HFD + Coptidis preparation (1 g/kg, p.o.), and HFD + lovastatin (50 mg/kg, p.o.) + Coptidis preparation (1 g/kg, p.o.) for 28 consecutive days. The pharmacokinetic results demonstrated that Coptidis preparation significantly augmented the conversion of lovastatin into its main metabolite lovastatin acid in vivo. The pharmacodynamic results revealed that the Coptidis preparation and half-dose lovastatin group reduced the body weight, liver weight, and visceral fat in HFD rats. These findings provide constructive preclinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic applications of Coptidis preparation on the benefit of hyperlipidemia.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isoflavones enhance pharmacokinetic exposure of active lovastatin acid via the upregulation of carboxylesterase in high-fat diet mice after oral administration of Xuezhikang capsules.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Nov;39(11):1804-1815. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0039-1. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29921884 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Berberine on promoting the excretion of cholesterol in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic hamsters.J Transl Med. 2015 Aug 27;13:278. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0629-3. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26310319 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Three Protoberberine-type Alkaloids from Raw and Bile-processed Rhizoma coptidis in Heat Syndrome Rats.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jan-Mar;13(49):51-57. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.197632. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28216883 Free PMC article.
-
[Exploring the mechanism of rhizoma coptidis in treating type II diabetes mellitus based on metabolomics by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2012 Jan;30(1):8-13. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1123.2011.08039. Se Pu. 2012. PMID: 22667084 Chinese.
-
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 May;32(5):403-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9160173 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Products for Cancer Therapy: A Review of Their Mechanism of Actions and Toxicity in the Past Decade.J Trop Med. 2022 Mar 11;2022:5794350. doi: 10.1155/2022/5794350. eCollection 2022. J Trop Med. 2022. PMID: 35309872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sukhorukov V. N.; Karagodin V. P.; Orekhov A. N. Modern methods of diagnosis dyslipidemia. Patol. Fiziol. Eksp. Ter. 2016, 60, 65–72. - PubMed
-
- Lauer M. S.; Fontanarosa P. B. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2001, 285, 2486–2497. 10.1001/jama.285.19.2486. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y.; Zhang H.; Chec E.; Zhang L.; Han J.; Yang Y.; Wang S.; Zhang M.; Gao C. Development of novel mesoporous nanomatrix-supported lipid bilayers for oral sustained delivery of the water-insoluble drug, lovastatin. Colloids Surf., B 2015, 128, 77–85. 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.02.021. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

