Modified National Early Warning Score as Early Predictor of Outcome in COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 34179692
- PMCID: PMC8211943
- DOI: 10.1007/s42399-021-00997-y
Modified National Early Warning Score as Early Predictor of Outcome in COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
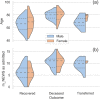
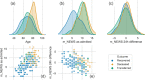
COVID-19 represented an important challenge to the Italian healthcare system (IHCS). Our main aim was to obtain evidence to support the use of modified national early warning score (m-NEWS) as an interdisciplinary, common, and universal scoring scale to quickly recognize patients with a risk of clinical deterioration before admission and during hospitalization. As a secondary goal, we tried to find a score threshold that can trigger patients' immediate medical review as a part of an optimal triaging protocol for an emergency setting where healthcare resources are overloaded. We performed a retrospective observational study. We included in our study all patients treated for COVID-19 infection in surgical departments between 01 March 2020 and 16 April 2020. Patients with negative test results for SARS-COV-2 were excluded. m-NEWS was obtained twice a day. Patients' m-NEWS were analyzed in order to verify the correlation between m-NEWS (at admission and m-NEWS variation 24 h after admission) and outcome (positive outcome-survival, negative outcome-death, or intensive care unit (ICU) transfer). We included a population-based sample of 225 SARS-COV-2-infected patients. Overall, the average age at hospitalization was 71 (ranging from 40 to 95). 144 (64%) patients were males and 81 (36%) females. m-NEWS values lower or equal to 7 were associated with the majority of the "recovered" population (100/132 75.75%) and at the same time with the minority of the "non-recovered" population (25/93 26.88%). For our sample, age is statistically correlated to the outcome but a triage protocol based solely on this variable is less effective than m-NEWS, which showed to be a reliable and easy-to-use score for first patient evaluation. Our observations pave the way towards further studies aiming at optimizing territorial and community healthcare management protocols.
Keywords: COVID-19; EWS; Respiratory failure; Score.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestAll authors declare that no support from any organization for the submitted work and no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years have been received. No other relationships or activities could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Regione Lombardia Emergenza Covid-19 - Avviso pubblico per manifestazione di interesse - Medici specialisti, medici specializzandi e medici laureati (2020) https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/portal/istituzionale/HP/DettaglioBa.... Accessed 03 march 2021
-
- Semeraro F, Scquizzato T, Scapigliati A, Ristagno G, Gamberini L, Tartaglione M, Dell’Arciprete O, Mora F, Cordenons F, del Giudice D, Picoco C, Gordini G. New Early Warning Score: off-label approach for Covid-19 outbreak patient deterioration in the community. Resuscitation. 2020;151:24–25. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2020.04.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Romero-Brufau S, Huddleston JM, Naessens JM, Johnson MG, Hickman J, Morlan BW, Jensen JB, Caples SM, Elmer JL, Schmidt JA, Morgenthaler TI, Santrach PJ. Widely used track and trigger scores: are they ready for automation in practice? Resuscitation. 2014;85:549–552. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2013.12.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
