Modeling in systems biology: Causal understanding before prediction?
- PMID: 34179849
- PMCID: PMC8212131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patter.2021.100280
Modeling in systems biology: Causal understanding before prediction?
Abstract
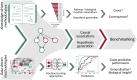
Babur et al. (2021) developed the CausalPath tool to infer causal signaling interactions in high-throughput proteomics data that may foster mechanical understanding from large-scale biological datasets.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
B.S. receives consultant fees from Turbine Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K., Mukherjee S., Ebert B.L., Gillette M.A., Paulovich A., Pomeroy S.L., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:15545–15550. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

