Cumulative delivery rate per aspiration IVF/ICSI cycle in POSEIDON patients: a real-world evidence study of 9073 patients
- PMID: 34179973
- PMCID: PMC8289325
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/deab152
Cumulative delivery rate per aspiration IVF/ICSI cycle in POSEIDON patients: a real-world evidence study of 9073 patients
Abstract
Study question: What is the cumulative delivery rate (CDR) per aspiration IVF/ICSI cycle in low-prognosis patients as defined by the Patient-Oriented Strategies Encompassing IndividualizeD Oocyte Number (POSEIDON) criteria?
Summary answer: The CDR of POSEIDON patients was on average ∼50% lower than in normal responders and varied across POSEIDON groups; differences were primarily determined by female age, number of embryos obtained, number of embryo transfer (ET) cycles per patient, number of oocytes retrieved, duration of infertility, and BMI.
What is known already: The POSEIDON criteria aim to underline differences related to a poor or suboptimal treatment outcome in terms of oocyte quality and quantity among patients undergoing IVF/ICSI, and thus, create more homogenous groups for the clinical management of infertility and research. POSEIDON patients are presumed to be at a higher risk of failing to achieve a live birth after IVF/ICSI treatment than normal responders with an adequate ovarian reserve. The CDR per initiated/aspiration cycle after the transfer of all fresh and frozen-thawed/warmed embryos has been suggested to be the critical endpoint that sets these groups apart. However, no multicenter study has yet substantiated the validity of the POSEIDON classification in identifying relevant subpopulations of patients with low-prognosis in IVF/ICSI treatment using real-world data.
Study design, size, duration: Multicenter population-based retrospective cohort study involving 9073 patients treated in three fertility clinics in Brazil, Turkey and Vietnam between 2015 and 2017.
Participants/materials, setting, methods: Participants were women with infertility between 22 and 42 years old in their first IVF/ICSI cycle of standard ovarian stimulation whose fresh and/or frozen embryos were transferred until delivery of a live born or until all embryos were used. Patients were retrospectively classified according to the POSEIDON criteria into four groups based on female age, antral follicle count (AFC), and the number of oocytes retrieved or into a control group of normal responders (non-POSEIDON). POSEIDON patients encompassed younger (<35 years) and older (35 years or above) women with an AFC ≥5 and an unexpected poor (<4 retrieved oocytes) or suboptimal (4-9 retrieved oocytes) response to stimulation, and respective younger and older counterparts with an impaired ovarian reserve (i.e. expected poor responders; AFC <5). Non-POSEIDON patients were those with AFC ≥5 and >9 oocytes retrieved. CDR was computed per one aspirated cycle. Logistic regression analysis was carried out to examine the association between patient classification and CDR.
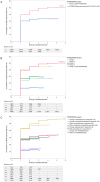
Main results and role of chance: The CDR was lower in the POSEIDON patients than in the non-POSEIDON patients (33.7% vs 50.6%; P < 0.001) and differed across POSEIDON groups (younger unexpected poor responder [Group 1a; n = 212]: 27.8%, younger unexpected suboptimal responder [Group 1b; n = 1785]: 47.8%, older unexpected poor responder [Group 2a; n = 293]: 14.0%, older unexpected suboptimal responder [Group 2b; n = 1275]: 30.5%, younger expected poor responder [Group 3; n = 245]: 29.4%, and older expected poor responder [Group 4; n = 623]: 12.5%. Among unexpected suboptimal/poor responders (POSEIDON Groups 1 and 2), the CDR was twice as high in suboptimal responders (4-9 oocytes retrieved) as in poor responders (<4 oocytes) (P = 0.0004). Logistic regression analysis revealed that the POSEIDON grouping, number of embryos obtained, number of ET cycles per patient, number of oocytes collected, female age, duration of infertility and BMI were relevant predictors for CDR (P < 0.001).
Limitations, reasons for caution: Our study relied on the antral follicle count as the biomarker used for patient classification. Ovarian stimulation protocols varied across study centers, potentially affecting patient classification.
Wider implications of the findings: POSEIDON patients exhibit lower CDR per aspirated IVF/ICSI cycle than normal responders; the differences are mainly determined by female age and number of oocytes retrieved, thereby reflecting the importance of oocyte quality and quantity. Our data substantiate the validity of the POSEIDON criteria in identifying relevant subpopulations of patients with low-prognosis in IVF/ICSI treatment. Efforts in terms of early diagnosis, prevention, and identification of specific interventions that might benefit POSEIDON patients are warranted.
Study funding/competing interest(s): Unrestricted investigator-sponsored study grant (MS200059_0013) from Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. The funder had no role in study design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish or manuscript preparation. S.C.E. declares receipt of unrestricted research grants from Merck and lecture fees from Merck and Med.E.A. H.Y. declares receipt of payment for lectures from Merck and Ferring. L.N.V. receives speaker fees and conferences from Merck, Merck Sharp and Dohme (MSD) and Ferring and research grants from MSD and Ferring. J.F.C. declares receipt of statistical services fees from ANDROFERT Clinic. T.M.H. received speaker fees and conferences from Merck, MSD and Ferring. P.H. declares receipt of unrestricted research grants from Merck, Ferring, Gedeon Richter and IBSA and lecture fees from Merck, Gedeon Richter and Med.E.A. C.A. declares receipt of unrestricted research grants from Merck and lecture fees from Merck. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Trial registration number: N/A.
Keywords: ART; POSEIDON criteria; cumulative delivery rate; embryo transfer; infertility; life table; live birth; real-world evidence.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antral follicle count and anti-Müllerian hormone to classify low-prognosis women under the POSEIDON criteria: a classification agreement study of over 9000 patients.Hum Reprod. 2021 May 17;36(6):1530-1541. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab056. Hum Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33822057
-
Cumulative live birth rates in low-prognosis women.Hum Reprod. 2019 Jun 4;34(6):1030-1041. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dez051. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31125412 Free PMC article.
-
The BISTIM study: a randomized controlled trial comparing dual ovarian stimulation (duostim) with two conventional ovarian stimulations in poor ovarian responders undergoing IVF.Hum Reprod. 2023 May 2;38(5):927-937. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dead038. Hum Reprod. 2023. PMID: 36864699 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: review and new classification criteria for reporting in clinical trials.Hum Reprod. 2016 Sep;31(9):1997-2004. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew149. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27343272 Review.
-
Higher probability of live-birth in high, but not normal, responders after first frozen-embryo transfer in a freeze-only cycle strategy compared to fresh-embryo transfer: a meta-analysis.Hum Reprod. 2019 Mar 1;34(3):491-505. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey388. Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30689865
Cited by
-
The influence of the pharmaceutical industry on the development of gonadotrophins and ovarian stimulation protocols in assisted reproductive technologies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 4;16:1536844. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1536844. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40255498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Male infertility.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023 Sep 14;9(1):49. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00459-w. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023. PMID: 37709866 Review.
-
Modelling futility in the setting of fertility treatment.Hum Reprod. 2022 May 3;37(5):877-883. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deac051. Hum Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35298646 Free PMC article.
-
Elective Single Cleavage-Stage Embryo Transfer in IVF Patients with Suboptimal Ovarian Response is Not Detrimental to Cumulative Pregnancy and Reduces Multiple Pregnancy Rates.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2023 Aug;73(4):329-335. doi: 10.1007/s13224-023-01768-6. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2023. PMID: 37701082 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of oestrogen pretreatment in patients with expected poor ovarian response (POSEIDON groups 3 and 4) undergoing GnRH antagonist protocol: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2023 Aug 9;13(8):e069840. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-069840. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37558441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alviggi C, Conforti A, Esteves SC, Vallone R, Venturella R, Staiano S, Castaldo E, Andersen CY, De Placido G.. Understanding ovarian hypo-response to exogenous gonadotropin in ovarian stimulation and its new proposed marker-the Follicle-To-Oocyte (FOI) index. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018;9:589. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg J.. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc: Ser B 1995;V57:289–300.
-
- Berker B, Şükür YE, Özdemir EÜ, Özmen B, Sönmezer M, Atabekoğlu CS, Aytaç R.. Human menopausal gonadotropin commenced on early follicular period increases live birth rates in POSEIDON group 3 and 4 poor responders. Reprod Sci 2021;28:488–494. - PubMed
-
- Bozdag G, Polat M, Yarali I, Yarali H.. Live birth rates in various subgroups of poor ovarian responders fulfilling the Bologna criteria. Reprod Biomed Online 2017;34:639–644. - PubMed
-
- Brandes M, van der Steen JO, Bokdam SB, Hamilton CJ, de Bruin JP, Nelen WL, Kremer JA.. When and why do subfertile couples discontinue their fertility care? A longitudinal cohort study in a secondary care subfertility population. Hum Reprod 2009;24:3127–3135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

