Eight-year outcomes for patients with aortic valve stenosis at low surgical risk randomized to transcatheter vs. surgical aortic valve replacement
- PMID: 34179981
- PMCID: PMC8347457
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab375
Eight-year outcomes for patients with aortic valve stenosis at low surgical risk randomized to transcatheter vs. surgical aortic valve replacement
Abstract
Aims: The aims of the study were to compare clinical outcomes and valve durability after 8 years of follow-up in patients with symptomatic severe aortic valve stenosis at low surgical risk treated with either transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) or surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR).
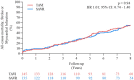
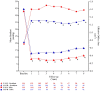
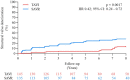
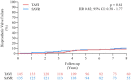
Methods and results: In the NOTION trial, patients with symptomatic severe aortic valve stenosis were randomized to TAVI or SAVR. Clinical status, echocardiography, structural valve deterioration, and failure were assessed using standardized definitions. In total, 280 patients were randomized to TAVI (n = 145) or SAVR (n = 135). Baseline characteristics were similar, including mean age of 79.1 ± 4.8 years and a mean STS score of 3.0 ± 1.7%. At 8-year follow-up, the estimated risk of the composite outcome of all-cause mortality, stroke, or myocardial infarction was 54.5% after TAVI and 54.8% after SAVR (P = 0.94). The estimated risks for all-cause mortality (51.8% vs. 52.6%; P = 0.90), stroke (8.3% vs. 9.1%; P = 0.90), or myocardial infarction (6.2% vs. 3.8%; P = 0.33) were similar after TAVI and SAVR. The risk of structural valve deterioration was lower after TAVI than after SAVR (13.9% vs. 28.3%; P = 0.0017), whereas the risk of bioprosthetic valve failure was similar (8.7% vs. 10.5%; P = 0.61).
Conclusions: In patients with severe aortic valve stenosis at low surgical risk randomized to TAVI or SAVR, there were no significant differences in the risk for all-cause mortality, stroke, or myocardial infarction, as well as the risk of bioprosthetic valve failure after 8 years of follow-up.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01057173.
Keywords: Bioprosthetic aortic valve durability; Mortality; Stroke; Surgical aortic valve replacement; Transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation or replacement? Valve durability in the context of patient life expectancy.Eur Heart J. 2021 Aug 7;42(30):2920-2923. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab393. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 34195813 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jørgensen TH. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients with lower surgical risk. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2020;13:332–334. - PubMed
-
- Thyregod HGH, Ihlemann N, Jørgensen TH, Nissen H, Kjeldsen BJ, Petursson P, Chang Y, Franzen OW, Engstrøm T, Clemmensen P, Hansen PB, Andersen LW, Steinbruüchel DA, Olsen PS, Søndergaard L. Five-year clinical and echocardiographic outcomes from the NOTION randomized clinical trial in patients at lower surgical risk. Circulation 2019;139:2714–2723. - PubMed
-
- Reardon MJ, Van Mieghem NM, Popma JJ, Kleiman NS, Søndergaard L, Mumtaz M, Adams DH, Deeb GM, Maini B, Gada H, Chetcuti S, Gleason T, Heiser J, Lange R, Merhi W, Oh JK, Olsen PS, Piazza N, Williams M, Windecker S, Yakubov SJ, Grube E, Makkar R, Lee JS, Conte J, Vang E, Nguyen H, Chang Y, Mugglin AS, Serruys PWJC, Kappetein AP; SURTAVI Investigators. Surgical or transcatheter aortic-valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1321–1331. - PubMed
-
- Popma JJ, Deeb GM, Yakubov SJ, Mumtaz M, Gada H, O'Hair D, Bajwa T, Heiser JC, Merhi W, Kleiman NS, Askew J, Sorajja P, Rovin J, Chetcuti SJ, Adams DH, Teirstein PS, Zorn GL, Forrest JK, Tchétché D, Resar J, Walton A, Piazza N, Ramlawi B, Robinson N, Petrossian G, Gleason TG, Oh JK, Boulware MJ, Qiao H, Mugglin AS, Reardon MJ; Evolut Low Risk Trial Investigators. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a self-expanding valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1706–1715. - PubMed
-
- Mack MJ, Leon MB, Thourani VH, Makkar R, Kodali SK, Russo M, Kapadia SR, Malaisrie SC, Cohen DJ, Pibarot P, Leipsic J, Hahn RT, Blanke P, Williams MR, McCabe JM, Brown DL, Babaliaros V, Goldman S, Szeto WY, Genereux P, Pershad A, Pocock SJ, Alu MC, Webb JG, Smith CR; PARTNER 3 Investigators. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1695–1705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

