[Research on characteristics of brain functional network in stroke patients during convalescent period under transcranial direct current stimulation]
- PMID: 34180195
- PMCID: PMC9927782
- DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.202010037
[Research on characteristics of brain functional network in stroke patients during convalescent period under transcranial direct current stimulation]
Abstract
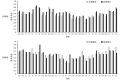
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is an emerging non-invasive brain stimulation technique. However, the rehabilitation effect of tDCS on stroke disease is unclear. In this paper, based on electroencephalogram (EEG) and complex network analysis methods, the effect of tDCS on brain function network of stroke patients during rehabilitation was investigated. The resting state EEG signals of 31 stroke rehabilitation patients were collected and divided into stimulation group (16 cases) and control group (15 cases). The Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated between the channels, brain functional network of two groups were constructed before and after stimulation, and five characteristic parameters were analyzed and compared such as node degree, clustering coefficient, characteristic path length, global efficiency, and small world attribute. The results showed that node degree, clustering coefficient, global efficiency, and small world attributes of brain functional network in the tDCS group were significantly increased, characteristic path length was significantly reduced, and the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.05). It indicates that tDCS can improve the brain function network of stroke patients in rehabilitation period, and may provide theory and experimental basis for the application of tDCS in stroke rehabilitation treatment.
经颅直流电刺激(tDCS)作为一种新兴的非侵入性脑刺激技术,对脑卒中疾病的康复作用目前尚未明确。本文结合脑电图(EEG)与复杂网络分析方法研究了 tDCS 对脑卒中患者康复期脑功能网络的影响。试验采集了 31 名脑卒中患者康复期的静息态 EEG 信号,其中 16 名患者作为试验组施加真刺激,15 名患者作为对照组施加伪刺激。利用皮尔逊相关系数法计算 EEG 信号之间的相关系数,并构建了两组受试者 tDCS 刺激前、后的脑功能网络,分析对比了不同状态下脑功能网络的节点度、聚类系数、特征路径长度、全局效率和“小世界”属性 5 个特征参数。结果发现,tDCS 真刺激后脑卒中患者脑功能网络的节点度、聚类系数、全局效率和“小世界”属性显著升高,特征路径长度显著降低,且差异具有统计学意义( P < 0.05)。该结果表明 tDCS 能够改善脑卒中患者康复期的脑功能网络,本研究可为 tDCS 应用于脑卒中康复治疗提供理论和试验依据。.
Keywords: brain function network; electroencephalogram; stroke; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突声明:本文全体作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
Figures








References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin E J, Go A S, et al Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):e38–e48. - PubMed
-
- 吴宏健, 李莉娜, 李龙, 等 脑卒中后手功能康复机器人综合干预研究进展. 生物医学工程学杂志. 2019;36(1):151–156.
-
- 王萌亚, 王仲朋, 陈龙, 等 卒中后运动神经反馈康复训练研究进展与前景. 中国生物医学工程学报. 2019;38(6):742–752. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2019.06.013. - DOI
-
- Raz J L, Soroker N, Friedman J, et al Effect of tDCS on reaching kinematics in subacute stroke patients. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2018;61:36–37.
-
- 杨冬菊, 王玉平 经颅直流电刺激技术及临床应用进展. 脑与神经疾病杂志. 2016;24(3):192–195.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
