Unique integrated stress response sensors regulate cancer cell susceptibility when Hsp70 activity is compromised
- PMID: 34180400
- PMCID: PMC8275131
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.64977
Unique integrated stress response sensors regulate cancer cell susceptibility when Hsp70 activity is compromised
Abstract
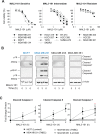
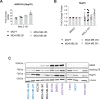
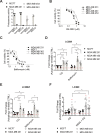
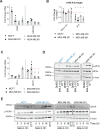
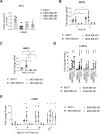
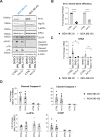
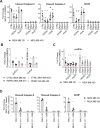
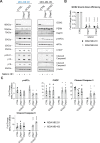
Molecular chaperones, such as Hsp70, prevent proteotoxicity and maintain homeostasis. This is perhaps most evident in cancer cells, which overexpress Hsp70 and thrive even when harboring high levels of misfolded proteins. To define the response to proteotoxic challenges, we examined adaptive responses in breast cancer cells in the presence of an Hsp70 inhibitor. We discovered that the cells bin into distinct classes based on inhibitor sensitivity. Strikingly, the most resistant cells have higher autophagy levels, and autophagy was maximally activated only in resistant cells upon Hsp70 inhibition. In turn, resistance to compromised Hsp70 function required the integrated stress response transducer, GCN2, which is commonly associated with amino acid starvation. In contrast, sensitive cells succumbed to Hsp70 inhibition by activating PERK. These data reveal an unexpected route through which breast cancer cells adapt to proteotoxic insults and position GCN2 and autophagy as complementary mechanisms to ensure survival when proteostasis is compromised.
Keywords: MAL3-101; apoptosis; autophagy; cell biology; human; molecular chaperone; proteostasis; unfolded protein response.
© 2021, Sannino et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SS, MY, MS, SO, AL, PW, JB No competing interests declared
Figures















References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

