Diagnostic accuracy of SPECT/CT arthrography in patients with suspected aseptic joint prostheses loosening
- PMID: 34181120
- PMCID: PMC8218161
- DOI: 10.1186/s41824-021-00098-y
Diagnostic accuracy of SPECT/CT arthrography in patients with suspected aseptic joint prostheses loosening
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of SPECT/CT arthrography in patients with suspected aseptic prosthesis loosening following hip and knee arthroplasty.
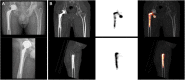
Methods: A retrospective review of 63 SPECT/CT arthrogram studies (36 knees and 27 hips) between February 1, 2013, and July 1, 2018, was conducted. All patients underwent clinical and radiologic evaluation as part of their assessment for persistent pain following hip and knee arthroplasty. The detection of tracer activity along the bone-prosthetic interface on SPECT/CT suggests aseptic loosening. Operative assessment as well as clinical/radiologic follow-up at a minimum of 1 year was used as the reference standard.
Results: The sensitivity and specificity of SPECT/CT for detection of aseptic loosening was 6/7 (86%) and 55/56 (98%), respectively. This gives a positive predictive value (PPV) of 6/7 (86%), a negative predictive value (NPV) of 55/56 (98%), and a diagnostic accuracy of 61/63 (97%).
Conclusion: SPECT/CT arthrography has a high diagnostic accuracy (97%) in the evaluation of loosening of both hip and knee arthroplasties in patients with persistent post-procedural pain.
Keywords: Loosening; SPECT/CT; Total hip arthroplasty; Total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
