CROssBAR: comprehensive resource of biomedical relations with knowledge graph representations
- PMID: 34181736
- PMCID: PMC8450100
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab543
CROssBAR: comprehensive resource of biomedical relations with knowledge graph representations
Abstract
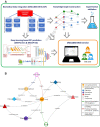
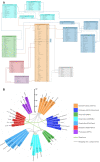
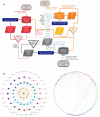
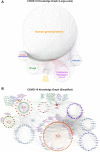
Systemic analysis of available large-scale biological/biomedical data is critical for studying biological mechanisms, and developing novel and effective treatment approaches against diseases. However, different layers of the available data are produced using different technologies and scattered across individual computational resources without any explicit connections to each other, which hinders extensive and integrative multi-omics-based analysis. We aimed to address this issue by developing a new data integration/representation methodology and its application by constructing a biological data resource. CROssBAR is a comprehensive system that integrates large-scale biological/biomedical data from various resources and stores them in a NoSQL database. CROssBAR is enriched with the deep-learning-based prediction of relationships between numerous data entries, which is followed by the rigorous analysis of the enriched data to obtain biologically meaningful modules. These complex sets of entities and relationships are displayed to users via easy-to-interpret, interactive knowledge graphs within an open-access service. CROssBAR knowledge graphs incorporate relevant genes-proteins, molecular interactions, pathways, phenotypes, diseases, as well as known/predicted drugs and bioactive compounds, and they are constructed on-the-fly based on simple non-programmatic user queries. These intensely processed heterogeneous networks are expected to aid systems-level research, especially to infer biological mechanisms in relation to genes, proteins, their ligands, and diseases.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Szklarczyk D., Gable A.L., Lyon D., Junge A., Wyder S., Huerta-Cepas J., Simonovic M., Doncheva N.T., Morris J.H., Bork P.et al. .. STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47:D607–D613. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

