Prognostic accuracy of a peripheral blood transcriptome signature in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- PMID: 34183448
- PMCID: PMC9246298
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-214790
Prognostic accuracy of a peripheral blood transcriptome signature in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Abstract
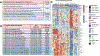
The prognostic value of peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) expression profiles, when used in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (CHP), as an adjunct to traditional clinical assessment is unknown. RNA-seq analysis on PBMC from 37 patients with CHP at initial presentation determined that (1) 74 differentially expressed transcripts at a 10% false discovery rate distinguished those with (n=10) and without (n=27) disease progression, defined as absolute FVC and/or diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) decline of ≥10% and increased fibrosis on chest CT images within 24 months, and (2) classification models based on gene expression and clinical factors strongly outperform models based solely on clinical factors (baseline FVC%, DLCO% and chest CT fibrosis).
Keywords: hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
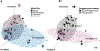
References
-
- Chung JH, Zhan X, Cao M, et al. Presence of air trapping and mosaic attenuation on chest computed tomography predicts survival in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2017;14:1533–8. - PubMed
-
- Fernández Pérez ER, Travis WD, Lynch DA, et al. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest. 2021;160(2):e97–e156 - PubMed
-
- Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, et al. Ct features of lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis: comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Radiology 2004;232:560–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
