MYD88, NFKB1, and IL6 transcripts overexpression are associated with poor outcomes and short survival in neonatal sepsis
- PMID: 34183713
- PMCID: PMC8238937
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92912-7
MYD88, NFKB1, and IL6 transcripts overexpression are associated with poor outcomes and short survival in neonatal sepsis
Abstract
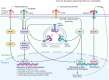
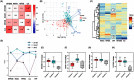
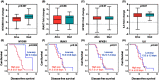
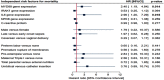
Toll-like receptor (TLR) family signature has been implicated in sepsis etiopathology. We aimed to evaluate the genetic profile of TLR pathway-related key genes; the myeloid differentiation protein 88 (MYD88), IL1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), the nuclear factor kappa-B1 (NFKB1), and interleukin 6 (IL6) in the blood of neonates with sepsis at the time of admission and post-treatment for the available paired-samples. This case-control study included 124 infants with sepsis admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit and 17 controls. The relative gene expressions were quantified by TaqMan Real-Time qPCR and correlated to the clinic-laboratory data. MYD88, NFKB1, and IL6 relative expressions were significantly higher in sepsis cases than controls. Higher levels of MYD88 and IL6 were found in male neonates and contributed to the sex-based separation of the cases by the principal component analysis. ROC analysis revealed MYD88 and NFKB1 transcripts to be good biomarkers for sepsis. Furthermore, patients with high circulatory MYD88 levels were associated with poor survival, as revealed by Kaplan-Meier curves analysis. MYD88, NFKB1, and IL6 transcripts showed association with different poor-outcome manifestations. Clustering analysis split the patient cohort into three distinct groups according to their transcriptomic signature and CRP levels. In conclusion, the study TLR pathway-related transcripts have a gender-specific signature, diagnostic, and prognostic clinical utility in neonatal sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utility of serum resistin in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and prediction of disease severity in term and late preterm infants.J Perinat Med. 2018 Oct 25;46(8):919-925. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2018-0018. J Perinat Med. 2018. PMID: 29605824
-
Validity of biomarkers in screening for neonatal sepsis - A single center -hospital based study.Pediatr Neonatol. 2019 Apr;60(2):149-155. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 12. Pediatr Neonatol. 2019. PMID: 29895470
-
Endocan and Soluble Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 as Novel Markers for Neonatal Sepsis.Pediatr Neonatol. 2015 Dec;56(6):415-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Pediatr Neonatol. 2015. PMID: 26341458
-
Expression of eight genes of nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in multiple myeloma using bone marrow aspirates obtained at diagnosis.Histol Histopathol. 2009 Aug;24(8):991-7. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.991. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19554506
-
Interleukin-6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis with premature rupture of the membranes: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(47):e13146. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013146. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30461611 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Component 1 Inhibitor Missense (Val480Met) Variant Is Associated With Gene Expression and Sepsis Development in Neonatal Lung Disease.Front Pediatr. 2022 May 20;10:779511. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.779511. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35669402 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs ANRIL and HOTAIR Upregulation is Associated with Survival in Neonates with Sepsis in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 20;15:6237-6247. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S373434. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35898301 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological validation of a novel exopolysaccharide from Streptomyces sp. 139 to effectively inhibit cytokine storms.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 9;10(14):e34392. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34392. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39816356 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the prognosis in patients with sepsis by a pyroptosis-related gene signature.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 21;13:1110602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1110602. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618365 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel compound IGYZT01060 for inhibition of IRAK-4 enzyme for the treatment of sepsis.Biotechnol Lett. 2025 Jun 14;47(3):62. doi: 10.1007/s10529-025-03604-5. Biotechnol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40515955
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

