Plasmodium falciparum phenotypic and genotypic resistance profile during the emergence of Piperaquine resistance in Northeastern Thailand
- PMID: 34183715
- PMCID: PMC8238947
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92735-6
Plasmodium falciparum phenotypic and genotypic resistance profile during the emergence of Piperaquine resistance in Northeastern Thailand
Abstract
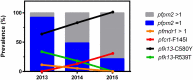
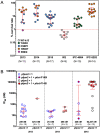
Malaria remains a public health problem in Thailand, especially along its borders where highly mobile populations can contribute to persistent transmission. This study aimed to determine resistant genotypes and phenotypes of 112 Plasmodium falciparum isolates from patients along the Thai-Cambodia border during 2013-2015. The majority of parasites harbored a pfmdr1-Y184F mutation. A single pfmdr1 copy number had CVIET haplotype of amino acids 72-76 of pfcrt and no pfcytb mutations. All isolates had a single pfk13 point mutation (R539T, R539I, or C580Y), and increased % survival in the ring-stage survival assay (except for R539I). Multiple copies of pfpm2 and pfcrt-F145I were detected in 2014 (12.8%) and increased to 30.4% in 2015. Parasites containing either multiple pfpm2 copies with and without pfcrt-F145I or a single pfpm2 copy with pfcrt-F145I exhibited elevated IC90 values of piperaquine. Collectively, the emergence of these resistance patterns in Thailand near Cambodia border mirrored the reports of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine treatment failures in the adjacent province of Cambodia, Oddar Meanchey, suggesting a migration of parasites across the border. As malaria elimination efforts ramp up in Southeast Asia, host nations militaries and other groups in border regions need to coordinate the proposed interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Malaria Report. (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

